Introduction to JBI
What is JBI?
TODO: Describe what the JBI specification is all about
Message Exchange Patterns
TODO: Describe the four standard JBI MEPs
JBI API
TODO: Describe the standard JBI API (MessageExchange, NormalizedMessage, ...)
JBI Components
servicemix-bean
Overview
The ServiceMix Bean component provides integration with beans (POJOs) with the JBI bus to make it easy to use POJOs to process JBI message exchanges. Like in an Message Driven Bean in J2EE a POJO will receive a message from the NMR and process it in any way it likes. Unlike in a JMS component where the coding is already done the Bean component gives the developer the freedom to create any type of message handling but it must be hand coded all the way.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/bean/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:bean="http://servicemix.apache.org/bean/1.0">
<bean:endpoint service="test:service" endpoint="endpoint" bean="#listenerBean"/>
<bean id="listenerBean" class="org.apache.servicemix.bean.beans.ListenerBean"/>
</beans></beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-bean component only defines one endpoint, called bean:endpoint. It can be used to receive and send message exchanges from/to the NMR.
Endpoint bean:endpoint
There are two ways to configure the bean endpoint. The first is using the fully qualified name of the class and the second is by passing to the endpoint a reference to an existing bean.
Using a Java class
When definining a bean:endpoint specifying a Java class name, a new instance of this class will be created for handling a single message exchange.
<beans xmlns:bean="http://servicemix.apache.org/bean/1.0"
xmlns:my="urn:org:servicmix:docs:examples">
<bean:endpoint service="my:service" endpoint="endpoint"
class="org.apache.servicemix.docs.bean.MyHandlerBean"/>
</beans>
Using a spring bean
Alternative, a reference to an existing bean can be passed to the bean endpoint.
<beans xmlns:bean="http://servicemix.apache.org/bean/1.0">
<bean:endpoint service="test:service" endpoint="endpoint" bean="#listenerBean"/>
<bean id="listenerBean" class="org.apache.servicemix.bean.beans.ListenerBean"/>
</beans>
Attention: The Bean Endpoint schema allows to set a Bean or a Bean Name. The Bean will create a single instance of the POJO per endpoint whereas the Bean Name will create an instance per request (message exchange).
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| applicationContext | org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext | Set the Spring ApplicationContext where the bean can be found. Defaults to the context defined in xbean.xml |
| bean | java.lang.Object | Set the bean to be used for handling exchanges |
| beanClassName | java.lang.String | Set the bean class name to be used for handling exchanges. A new instance will be created on the fly for every exchange. |
| beanInfo | org.apache.servicemix.bean.support.BeanInfo | Set a custom bean info object to define the bean to be used for handling exchanges |
| beanName | java.lang.String | Set the name of the bean in the application context to be used for handling exchanges |
| beanType | java.lang.Class | Set the bean class to be used for handling exchanges. A new instance will be created on the fly for every exchange. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.bean.BeanComponent | |
| correlationExpression | org.apache.servicemix.expression.Expression | Set a custom expression to use for correlating exchanges into a single request handled by the same bean instance. The default expression uses a correlation ID set on the exchange properties. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| methodInvocationStrategy | org.apache.servicemix.bean.support.MethodInvocationStrategy | Set a custom invocation strategy to define how the bean is being invoked. The default implementation takes some additional parameter annotations into account. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| serviceEndpoint | javax.jbi.servicedesc.ServiceEndpoint |
MessageExchangeListener
The first kind of POJOs you can deploy implement the MessageExchagneListener interface. In such a case, servicemix-bean acts as a replacement of the lightweight container component. This level offers the most control on the exchange received and sent. This is usually used with the injected DeliveryChannel to send back the exchanges, or if the POJOs needs to act as a consumer (i.e. creating and sending exchanges to other services).
These POJOs are low-level POJOs: you need to understand the JBI Api and Message Exchange Patterns to correctly handle incoming exchanges.
Note that at this point (v 3.1), there is no base class that you can inherit to speed you in this process of implementing a POJO to handle JBI exchanges, but hopefully it will come in the future.
Examples
This example on the right shows the most simple bean. When it receives an exchange, it will print it to the console and set the status to DONE before sending the exchange back. This bean can not handle InOut exchanges, as it does not set any response (an exception would be thrown in such a case).
import org.apache.servicemix.jbi.listener.MessageExchangeListener;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.jbi.messaging.DeliveryChannel;
import javax.jbi.messaging.ExchangeStatus;
import javax.jbi.messaging.MessageExchange;
import javax.jbi.messaging.MessagingException;
public class ListenerBean implements MessageExchangeListener {
@Resource
private DeliveryChannel channel;
public void onMessageExchange(MessageExchange exchange) throws MessagingException {
System.out.println("Received exchange: " + exchange);
exchange.setStatus(ExchangeStatus.DONE);
channel.send(exchange);
}
}
This example will handle an InOut exchange and will send back the input as the response.
Note that this example would fail if receiving an InOnly exchange, as setting a response on an InOnly exchange is not a legal operation.
import org.apache.servicemix.jbi.listener.MessageExchangeListener;
import org.apache.servicemix.jbi.util.MessageUtil;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.jbi.messaging.DeliveryChannel;
import javax.jbi.messaging.ExchangeStatus;
import javax.jbi.messaging.MessageExchange;
import javax.jbi.messaging.MessagingException;
public class ListenerBean implements MessageExchangeListener {
@Resource
private DeliveryChannel channel;
public void onMessageExchange(MessageExchange exchange) throws MessagingException {
if (exchange.getStatus() == ExchangeStatus.ACTIVE) {
MessageUtil.transferInToOut(exchange, exchange);
channel.send(exchange);
}
}
}
This is similar example as the one from above (also works only for InOut exchange) but it shows how you can extract message from an exchange in order to process it and send back.
import org.apache.servicemix.jbi.listener.MessageExchangeListener;
import org.apache.servicemix.jbi.util.MessageUtil;
import org.apache.servicemix.jbi.jaxp.SourceTransformer;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.jbi.messaging.DeliveryChannel;
import javax.jbi.messaging.ExchangeStatus;
import javax.jbi.messaging.MessageExchange;
import javax.jbi.messaging.MessagingException;
import javax.jbi.messaging.NormalizedMessage;
import javax.xml.transform.Source;
public class ListenerBean implements MessageExchangeListener {
@Resource
private DeliveryChannel channel;
public void onMessageExchange(MessageExchange exchange) throws MessagingException {
if (exchange.getStatus() == ExchangeStatus.ACTIVE) {
NormalizedMessage message = exchange.getMessage("in");
Source content = message.getContent();
//process content according to your logic
//e.g. to access the message body as a String use
String body = (new SourceTransformer()).toString(content);
message.setContent(content);
exchange.setMessage(message, "out");
channel.send(exchange);
}
}
}
Disclaimer
In versions 3.1 to 3.1.2 the ServiceMix Bean component will not handle asynchronous messages correctly because the final send of the message marked as DONE back to the NMR will be handled as a consumer message and that fails because there is no corresponding provider message. The only workaround is to send the messages synchronously.
Note: This was resolved in 3.1.3, 3.2.x and later via SM-1110.
MessageExchange dispatching
If the POJO deployed implements the org.apache.servicemix.MessageExchangeListener, every message received for this POJO will be dispatched to the onMessageExchange method.
In other cases, exchanges in a provider role will be dispatched according to the MethodInvocationStrategy configured on the endpoint. The default one try to find the method according to the operation name defined on the exchange. If there is only a single method acting as an operation, it will always be used.
Annotations
The servicemix-bean component can accept different kind of POJOs. These POJOs may be annotated to customize their behavior. All the following annotations belong to the org.apache.servicemix.bean package.
| Annotation | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Callback | Method | |
| Content | Parameter | |
| Correlation | Type | |
| Endpoint | Type | This annotation is mandatory if the bean is automatically searched from a list of packages. |
| ExchangeTarget | Field | |
| Operation | Method | |
| Property | Parameter | |
| XPath | Parameter |
In addition, standard annotations can be used:
| Annotation | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Resource | Field | The Resource annotation marks a resource that is needed by the application. Currently, this annotation is only supported on fields of type ComponentContext and DeliveryChannel. The component will inject the specified resource when the POJO is instantiated. |
| PostConstruct | Method | The PostConstruct annotation is used on a method that needs to be executed after dependency injection is done to perform any initialization. |
| PreDestroy | Method | The PreDestroy annotation is used on methods as a callback notification to signal that the instance is in the process of being removed by the container. |
The following interfaces are part of this API:
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| MessageExchangeListener | When the POJO implements this interface, all exchanges will be dispatched to the onMessageExchange method. |
| Destination | This interface can be used to define a property on the bean, annotated with the @ExchangeTarget annotation. This is a very simple API to send exchanges from a POJO. More complex use cases can use an injected DeliveryChannel directly or to create a ServiceMix client. |
More Examples
servicemix-camel
Overview
The servicemix-camel component provides support for using Apache Camel to provide a full set of Enterprise Integration Patterns and flexible routing and transformation in both Java code or Spring XML to route services on the Normalized Message Router.
Namespace and camel-context.xml
When creating a servicemix-camel service unit, we reuse the default Camel namespace http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring.
This is an example camel-context.xml which uses the Spring DSL to define the Camel routes
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd">
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring">
<route>
<!-- route defined in the Spring DSL -->
</route>
</camelContext>
</beans>
It is also possible to use the Java DSL inside a servicemix-camel service unit by referring to the package that contains the RouteBuilder classes. An example: this camel-context.xml file will activate all routes defined by RouteBuilders in the org.apache.servicemix.example.camel package.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd">
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring">
<packages>org.apache.servicemix.examples.camel</packages>
</camelContext>
</beans>
URI
Camel routes use URIs to interact with the ESB. You can use these URIs to expose new endpoints on the ESB as well as to send message exchanges to existing endpoints.
The snippet below automatically exposes a new endpoint to the bus, where the service QName is MyService and the endpoint name is MyEndpoint.
from("jbi:endpoint:http://foo.bar.org/MyService/MyEndpoint")
When a JBI endpoint appears at the end of a route, as in the example below, that will send
to("jbi:endpoint:http://foo.bar.org/MyService/MyEndpoint")
The messages sent by this producer endpoint are sent to the already deployed JBI endpoint.
URI format
jbi:service:serviceNamespace[sep]serviceName[?options]
jbi:endpoint:serviceNamespace[sep]serviceName[sep]endpointName[?options]
jbi:name:endpointName[?options]
The separator that should be used in the endpoint URL is:
/ (forward slash), if serviceNamespace starts with http://
: (colon), if serviceNamespace starts with urn:.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&ption=value&..
Examples
Using jbi:service
jbi:service:http://foo.bar.org/MyService
jbi:service:urn:foo:bar:MyService
Using jbi:endpoint
jbi:endpoint:urn:foo:bar:MyService:MyEndpoint
jbi:endpoint:http://foo.bar.org/MyService/MyEndpoint
Using jbi:name
When using jbi:name, the component uses http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/jbi}endpoint as the default Service QName.
jbi:name:MyEndpoint
URI options
| Name | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mep | MEP of the Camel Exchange | Allows users to override the MEP set on the Exchange object. Valid values for this option are in-only, in-out, robust-in-out and in-optional-out. |
| operation | Value of the jbi.operation header property | Specifies the JBI operation for the MessageExchange. If no value is supplied, the JBI binding will use the value of the jbi.operation header property. |
| serialization | basic | Default value (basic) will check if headers are serializable by looking at the type, setting this option to strict will detect objects that can not be serialized although they implement the Serializable interface. Set to nocheck to disable this check altogether, note that this should only be used for in-memory transports like SEDAFlow, otherwise you can expect to get NotSerializableException thrown at runtime. |
| convertException | false | false: send any exceptions thrown from the Camel route back unmodified true: convert all exceptions to a JBI FaultException (can be used to avoid non-serializable exceptions or to implement generic error handling |
Examples
jbi:service:http://foo.bar.org/MyService?mep=in-out (override the MEP, use InOut JBI MessageExchanges)
jbi:endpoint:urn:foo:bar:MyService:MyEndpoint?mep=in (override the MEP, use InOnly JBI MessageExchanges)
jbi:endpoint:urn:foo:bar:MyService:MyEndpoint?operation={http://www.mycompany.org}AddNumbers
(overide the operation for the JBI Exchange to {http://www.mycompany.org}AddNumbers)
Example routes
Simple Spring route
This simple Spring route registers a new endpoint on the ESB (service Router, endpoint name orders). The message exchange contents will be logged and then forwarded to another JBI service endpoint (service OrderService)
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd">
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring">
<route>
<from uri="jbi:endpoint:urn:org:example:Router:orders"/>
<to uri="log:OrderLogging"/>
<to uri="jbi:service:http://services.example.org/OrderService" />
</route>
</camelContext>
</beans>
The same route using the Java DSL
When we implement the same route in the Java DSL, we first code our RouteBuilder implementation
package org.apache.servicemix.example;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
public class JbiRouteBuilder extends RouteBuilder {
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("jbi:endpoint:urn:org:example:Router:orders")
.to("log:OrderLogging")
.to("jbi:service:http://services.example.org/OrderService");
}
}
In our camel-context.xml file, we just refer to the org.apache.servicemix.example package that contains our JbiRouteBuilder.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd">
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring">
<route>
<packageScan>
<package>org.apache.servicemix.example</package>
</packageScan>
</route>
</camelContext>
</beans>
Special considerations
Stream handling
If you are using a stream type as the message body, you should be aware that a stream is only capable of being read once. So if you enable DEBUG logging, the body is usually logged and thus read. To deal with this, Camel has a streamCaching option that can cache the stream, enabling you to read it multiple times.
from("jbi:endpoint:http://foo.bar.org/MyService/MyEndpoint")
.streamCaching()
.to("xslt:transform.xsl", "bean:doSomething");
Camel will cache large input streams (by default, over 64K) in a temp file using CachedOutputStream. When you close the input stream, the temp file will be deleted.
servicemix-cxf-bc
Overview
A JBI compliant HTTP/SOAP or JMS/SOAP binding component named servicemix-cxf-bc which use apache cxf internally.
The main features are:
JBI compliant Binding Component
Usable in a lightweight mode in servicemix.xml configuration files
SOAP 1.1 and 1.2 support
MIME attachments
Support for all MEPs as consumers or providers
SSL support
WS-Security support
WS-Policy support
WS-RM support
WS-Addressing support
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/cxfbc/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:cxfbc="http://servicemix.apache.org/cxfbc/1.0">
<!-- add cxfbc:consumer or cxfbc:provider definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-cxf-bc component defines two endpoints:
cxfbc:consumer :: a server-side cxf endpoint that will consume plain HTTP+SOAP requests and send them into the NMR to a given JBI endpoint
cxfbc:provider :: a client-side jbi endpoint which can receive requests from the NMR and send them to a given url where the service is provided
cxfbc:consumer
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| busCfg | java.lang.String | the location of the CXF configuration file used to configure the CXF bus. This allows you to configure features like WS-RM and JMS runtime behavior. |
| delegateToJaas | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint delegate to JAASAuthenticationService to do the authentication. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| features | (java.lang.Object)\* | Specifies the cxf features set for this endpoint |
| inFaultInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process incoming faults |
| inInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process incoming responses |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| locationURI | java.lang.String | the HTTP address to which requests are sent. This value will overide any value specified in the WSDL. |
| mtomEnabled | boolean | Specifies if MTOM / attachment support is enabled. Default is <code>false</code>. |
| outFaultInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process fault messages being returned to the consumer |
| outInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process requests |
| properties | java.util.Map | Sets arbitrary properties that are added to the CXF context at the Endpoint level |
| providedBus | org.apache.cxf.Bus | a preconfigured CXF Bus object to use; overrides busCfg |
| schemaValidationEnabled | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint use schemavalidation for the incoming/outgoing message. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| synchronous | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint expects send messageExchange by sendSync . |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
| timeout | long | the number of second the endpoint will wait for a response. The default is unlimited. |
| useJBIWrapper | boolean | Specifies if the JBI wrapper is sent in the body of the message. Default is <code>true</code>. |
| useSOAPEnvelope | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint expects soap messages when useJBIWrapper is false, |
| wsdl | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | the location of the WSDL document defining the endpoint's interface |
| x509 | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint use X.509 Certificate to do the authentication. |
cxfbc:provider
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| busCfg | java.lang.String | the location of the CXF configuration file used to configure the CXF bus. This allows you to configure features like WS-RM and JMS runtime behavior. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| features | (java.lang.Object)\* | Specifies the cxf features set for this endpoint |
| inFaultInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process incoming faults |
| inInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process incoming requests |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| locationURI | java.net.URI | the HTTP address of the exposed service. This value will overide any value specified in the WSDL. |
| mtomEnabled | boolean | Specifies if MTOM / attachment support is enabled. Default is <code>false</code>. |
| outFaultInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process fault messages being returned to the consumer |
| outInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process responses |
| properties | java.util.Map | Sets arbitrary properties that are added to the CXF context at the Endpoint level |
| providedBus | org.apache.cxf.Bus | a preconfigured CXF Bus object to use; overrides busCfg |
| schemaValidationEnabled | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint use schemavalidation for the incoming/outgoing message. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| synchronous | boolean | Specifies if the endpoints send message synchronously to external server using underlying |
| useJBIWrapper | boolean | Specifies if the JBI wrapper is sent in the body of the message. Default is <code>true</code>. |
| useSOAPEnvelope | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint expects soap messages when useJBIWrapper is false, |
| wsdl | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | the location of the WSDL document defining the endpoint's interface |
Examples
Configuring the CXF JMS Transport
The ServiceMix CXF binding component also allows using the CXF JMS Transport to send and receive messages. You can use the <cxf:features/> element to add and configure the org.apache.cxf.transport.jms.JMSConfigFeature on the endpoint, as in the example below.
<cxfbc:provider wsdl="org/apache/servicemix/cxfbc/ws/security/hello_world.wsdl"
service="greeter:HelloWorldService"
endpoint="HelloWorldPortProxy"
interfaceName="greeter:Greeter"
busCfg="jms_conduit_config.xml">
<!-- add interceptors here -->
<cxfbc:features>
<bean class="org.apache.cxf.transport.jms.JMSConfigFeature">
<property name="jmsConfig">
<bean class="org.apache.cxf.transport.jms.JMSConfiguration">
<property name="concurrentConsumers">
<value>5</value>
</property>
<property name="connectionFactory">
<ref bean="myConnectionFactory" />
</property>
<property name="targetDestination">
<value>test.jmstransport.text.provider</value>
</property>
<property name="useJms11">
<value>false</value>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</cxfbc:features>
</cxfbc:provider>
<amq:connectionFactory id="myConnectionFactory" brokerURL="vm://localhost"/>
The jms_conduit_config.xml file specified in the busCfg parameter, is optional and can be used to specify additional JMS transport parameters:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jms="http://cxf.apache.org/transports/jms"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://cxf.apache.org/transports/jms http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/configuration/jms.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<jms:conduit name="{http://apache.org/hello_world_soap_http}HelloWorldPort.jms-conduit" abstract="true">
<jms:clientConfig clientReceiveTimeout="200000"/>
</jms:conduit>
</beans>
Configuring the CXF HTTP Transport
In order to configure the underlying HTTP transport used by a CXF BC endpoint, you can specify an additional busCfg file as in the example below.
<cxfbc:provider wsdl="org/apache/servicemix/cxfbc/ws/security/hello_world.wsdl"
service="greeter:HelloWorldService"
endpoint="HelloWorldPortProxy"
interfaceName="greeter:Greeter"
busCfg="http_conduit_config.xml">
<!-- add interceptors and additional CXF features here -->
</cxfbc:provider>
The http_conduit_config.xml file can then specify the additional CXF configuration. Have a look at this page for an overview of all the options supported by CXF.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:http-conf="http://cxf.apache.org/transports/http/configuration"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://cxf.apache.org/transports/http/configuration
http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/configuration/http-conf.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<http-conf:conduit name="{http://apache.org/hello_world_soap_http}HelloWorldPort.http-conduit">
<http-conf:client Connection="Keep-Alive"
MaxRetransmits="1"
AllowChunking="false" />
</http-conf:conduit>
</beans>
servicemix-cxf-se
Overview
ServiceMix CXF SE component is a JBI Service Engine exposing (annotated) POJO as services on the JBI Bus.
It uses Apache CXF internally to perform service invocations and xml marshaling.
Features:
jsr181 annotations
jaxb2/aegis/xmlbeans databinding
wsdl auto generation
java proxy support
MTOM / attachments support
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/cxfse/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:cxfse="http://servicemix.apache.org/cxfse/1.0">
<!-- add cxfse:endpoint definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-cxf-bc component defines one endpoint type:
cxfse:endpoint :: no description yet
cxfse:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| inFaultInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process incoming faults |
| inInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process incoming requests |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| mtomEnabled | boolean | Specifies if the service can consume MTOM formatted binary data. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| outFaultInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process fault messages being returned to the consumer |
| outInterceptors | (java.lang.Object)\* | a list of beans configuring interceptors that process response messages |
| pojo | java.lang.Object | a bean configuring the JAX-WS annotated implementation for the endpoint |
| pojoEndpoint | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Specifies the servicemodel endpoint name generated from the pojo. The default is <code>null</code>. |
| pojoInterfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Specifies the servicemodel interface name generated from the pojo. The default is <code>null</code>. |
| pojoService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Specifies the servicemodel service name generated from the pojo. The default is <code>null</code>. |
| properties | java.util.Map | Specifies a map of properties |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| useAegis | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint use aegis databinding to marshall/unmarshall message. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| useJBIWrapper | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint expects to receive the JBI wrapper in the message received from the NMR. The default is <code>true</code>. Ignore the value of useSOAPEnvelope if useJBIWrapper is true |
| useSOAPEnvelope | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint expects soap messages when useJBIWrapper is false, if useJBIWrapper is true then ignore useSOAPEnvelope. The default is <code>true</code>. |
| useXmlBeans | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint use xmlbeans databinding to marshell/unmarshell message. The default is <code>false</code>. |
cxfbc:proxy
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| componentRegistry | java.lang.Object | Allows injecting a custom component registry for looking up the proxying endpoint. |
| container | org.apache.servicemix.jbi.api.Container | Allows injecting a JBI Container instance (e.g. for testing purposes). |
| context | javax.jbi.component.ComponentContext | Allows injecting the ComponentContext |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| factory | org.apache.servicemix.jbi.api.ClientFactory | Allows injecting a ClientFactory |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Specifies the servicemodel interface name |
| mtomEnabled | boolean | Specifies if the service can consume MTOM formatted binary data. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| name | java.lang.String | Specifies the JNDI name for looking up the ClientFactory. Defaults to <code>java:comp/env/jbi/ClientFactory</code>. |
| propagateSecuritySubject | boolean | When set to <code>true</code>, the security subject is propagated along to the proxied endpoint. Defaults to <code>false</code>. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Specifies the servicemodel service name |
| type | java.lang.Class | Specifies the webservice POJO type |
| useJBIWrapper | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint expects to receive the JBI wrapper in the message received from the NMR. The default is <code>true</code>. Ignore the value of useSOAPEnvelope if useJBIWrapper is true |
| useSOAPEnvelope | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint expects soap messages when useJBIWrapper is false, if useJBIWrapper is true then ignore useSOAPEnvelope. The default is <code>true</code>. |
servicemix-drools
Overview
The ServiceMix Drools component provides JBI integration to the Drools Rules Engine.
This Service Engine can be used to deploy a rules set that will implement a router or an actual service.
A router will mostly act as a transparent proxy between the consumer and the target service provider mad will mostly be implemented by the jbi.route(uri) method below. This method creates a new exchange identical to the one received by the component and will send it to the specified destination. You can also send back a Fault if needed. A router can also be implemented by using directly the JBI Apis (available with the jbi helper) by using the provided client.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/drools/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:drools="http://servicemix.apache.org/drools/1.0">
<!-- add drools:endpoint definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-drools component defines one endpoint type:
drools:endpoint :: no description yet
drools:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| assertedObjects | (java.lang.Object)\* | List of additional objects to be inserted into the drools working memory for evaluating rules. |
| autoReply | boolean | Will this endpoint automatically reply to any exchanges not handled by the Drools rulebase? |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | |
| defaultTargetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The default service that the exchange will be sent to if none of the rules have handled it. |
| defaultTargetURI | java.lang.String | The default endpoint URI that the exchange will be sent to if none of the rules have handled it. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| globals | java.util.Map | The global variables that are available while evaluating the rule base. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| namespaceContext | javax.xml.namespace.NamespaceContext | The namespace context to use when evaluating the rules. |
| ruleBase | org.drools.RuleBase | Set the rule base to be used for handling the exchanges |
| ruleBaseResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Specifies the resource location to load the rule base from (.drl file) |
| ruleBaseURL | java.net.URL | Specifies a URL to load the rule base from (.drl file) |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| su | org.apache.servicemix.common.ServiceUnit |
servicemix-eip
Overview
The servicemix-eip component is a routing container where different routing patterns can be deployed as service unit.
This component is based on the great Enterprise Integration Patterns book.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/eip/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix eip.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:eip="http://servicemix.apache.org/eip/1.0"
xsi:schemalocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<!-- Pipeline example -->
<eip:pipeline service="test:pipeline" endpoint="endpoint">
<eip:transformer>
<eip:exchange-target service="test:transformer" />
</eip:transformer>
<eip:target>
<eip:exchange-target service="test:trace" />
</eip:target>
</eip:pipeline>
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-eip component defines several endpoint types:
eip:content-based-router :: Implements the Content-Based Router EIP
eip:message-filter :: Implements the Message Filter EIP
eip:pipeline :: Implements the Pipeline EIP
eip:static-recipient-list :: Implements the Static Recipient List EIP
eip:static-routing-slip :: Implements the Static Routing Slip EIP
eip:wire-tap :: Implements the Wire Tap EIP
eip:xpath-splitter :: Uses XPath to split a message
eip:split-aggregator :: Aggregates messages that have been split by the xpath-splitter
eip:content-enricher :: Implements the Content Enricher EIP
eip:resequencer :: Implements the Resequencer EIP
eip:async-bridge :: Handles an InOut exchange by correlating to separate InOnly exchanges
In addition, this component can use all ServiceMix flows (including clustered and transactional flows), can be configured to be resilient to crashes and supports full fail-over to another node when clustered.
Content Based Router
ContentBasedRouter can be used for all kind of content-based routing.
This pattern implements the Content-Based Router pattern.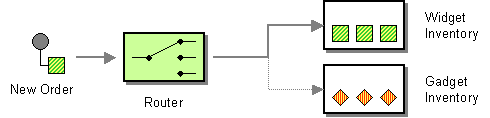
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| forwardOperation | boolean | Forward the operation qname when sending the exchange to the target. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| rules | (org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.RoutingRule)\* | The list of routing rules. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
Message Filter
MessageFilter allows filtering incoming JBI exchanges. As it drops unwanted messages and in an InOut exchange a response is required, MessageFilter and InOut MEPs cannot be used together.
This pattern implements the Message Filter pattern.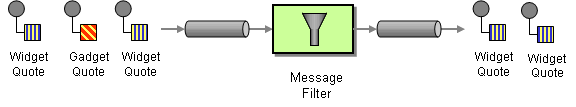
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| filter | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.Predicate | The filter to use on incoming messages |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| reportErrors | boolean | Indicates if faults and errors from recipients should be sent back to the consumer. In such a case, only the first fault or error received will be reported. Note that if the consumer is synchronous, it will be blocked until all recipients successfully acked the exchange, or a fault or error is reported, and the exchange will be kept in the store for recovery. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| target | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The main target destination which will receive the exchange |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
Pipeline
The Pipeline component is a bridge between an In-Only (or Robust-In-Only) MEP and an In-Out MEP. When the Pipeline receives an In-Only MEP, it will send the input in an In-Out MEP to the tranformer destination and forward the response in an In-Only MEP to the target destination.
The old org.apache.servicemix.components.util.PipelineComponent will be deprecated. This one offers the same feature but can be safely clustered and use in a transactional enviromnent.
In the default configuration, faults sent by the transformer component are sent back to the consumer as faults if the exchange MEP supports them, or as errors (for InOnly exchanges). This behavior can be changed by setting the sendFaultsToTarget attribute to true, in which case faults will be sent to the target component, or by adding a faultsTarget element where faults should be sent.
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| copyAttachments | boolean | Should message attachments be copied ? |
| copyProperties | boolean | Should message properties be copied ? |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| faultsTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The address of the endpoint to send faults to |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| sendFaultsToTarget | boolean | When the faultsTarget is not specified, faults may be sent to the target endpoint if this flag is set to <code>true</code> |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| target | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The address of the target endpoint |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| transformer | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The adress of the in-out endpoint acting as a transformer |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
Static Recipeint List
The StaticRecipientList component will forward an input In-Only or Robust-In-Only exchange to a list of known recipients.
This component implements the Recipient List pattern, with the limitation that the recipient list is static.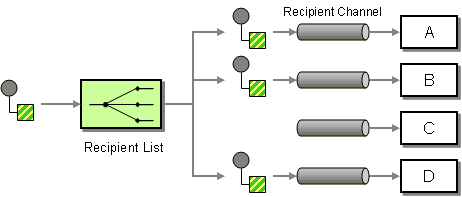
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| recipients | (org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget)\* | A list of recipients that will each receive a copy of the input message. |
| reportErrors | boolean | Indicates if faults and errors from recipients should be sent back to the consumer. In such a case, only the first fault or error received will be reported. Note that if the consumer is synchronous, it will be blocked until all recipients successfully acked the exchange, or a fault or error is reported, and the exchange will be kept in the store for recovery. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
Static Routing Slip
A RoutingSlip component can be used to route an incoming In-Out exchange through a series of target services.
This component implements the Routing Slip pattern, with the limitation that the routing table is static.
This component only uses In-Out MEPs and errors or faults sent by targets are reported back to the consumer, thus interrupting the routing process.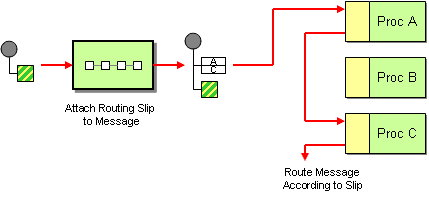
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| targets | (org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget)\* | List of target endpoints used in the RoutingSlip |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
Wire Tap
A WireTap component can be used to forward a copy of the input message to a listener in a proxy fashion.
This component implements the WireTap pattern.
It can handle all four standard MEPs, but will only send an In-Only MEP to the listener.
The originating service must be configured to send messages to the WireTap directly.
In the case of an In-Out MEP, this means that the WireTap needs to be configured to send the exchange along to the destination service.
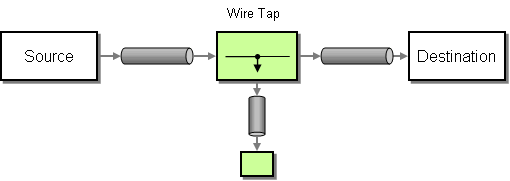
Similar to the example above, the WireTap can also be used:
to forward the output message of an exchange using <eip:outListener/>
to forward the fault message of an exchange using <eip:faultListener/>
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| copyProperties | boolean | If copyProperties is <code>true</code>, properties on the in message will be copied to the out / fault message before it is sent. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| faultListener | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The listener destination for fault messages |
| inListener | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The listener destination for in messages |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| outListener | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The listener destination for out messages |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| target | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The main target destination which will receive the exchange |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
XPath Splitter
The XPathSplitter component implements the Splitter pattern using an xpath expression to split the incoming xml.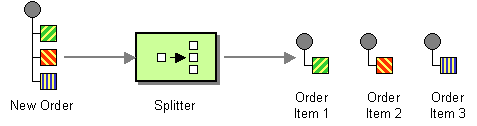
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| factory | javax.xml.xpath.XPathFactory | The XPath factory. If no factory is explicitely configured, a defaut one will be created using <code>XPathFactory.newInstance()</code>. |
| forwardAttachments | boolean | Indicates if incoming attachments should be forwarded with the new exchanges. |
| forwardProperties | boolean | Indicates if properties on the incoming message should be forwarded. |
| functionResolver | javax.xml.xpath.XPathFunctionResolver | The function resolver. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| namespaceContext | javax.xml.namespace.NamespaceContext | The namespace context to use when evaluating the xpath expression |
| reportErrors | boolean | Indicates if faults and errors from splitted parts should be sent back to the consumer. In such a case, only the first fault or error received will be reported. Note that if the consumer is synchronous, it will be blocked until all parts have been successfully acked, or a fault or error is reported, and the exchange will be kept in the store for recovery. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| synchronous | boolean | Specifies wether exchanges for all parts are sent synchronously or not. |
| target | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The address of the target endpoint. |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| variableResolver | org.apache.servicemix.expression.MessageVariableResolver | The variable resolver. The default one will enable the use of properties on the message, exchange, as well as making system properties and environment properties available. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
| xpath | java.lang.String | The xpath expression used to split the input message. |
Split Aggregator
The SplitAggregator is an aggregator mainly usefull to collect messages that have been created using a splitter.
It relies on several properties that should be set on the exchanges (count, index, correlationId).
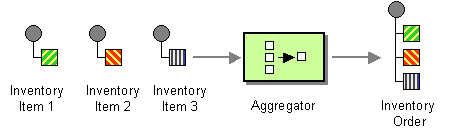
Endpoint properties
Content Enricher
With a Content Enricher you can extract additional information from a source and add this information to your message. This is useful if the calling service for example extracts a 'userID' and your target system is only aware of a 'userName'. By using the Content-Enricher you could extract this information from a source system and add this additional information ('userName') to your message.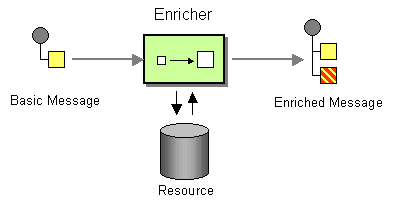
<eip:content-enricher service="test:contentEnricher" endpoint="endpoint">
<eip:enricherTarget>
<eip:exchange-target service="test:additionalInformationExtracter" />
</eip:enricherTarget>
<eip:target>
<eip:exchange-target service="test:myTarget" />
</eip:target>
</eip:content-enricher>
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| copyAttachments | boolean | If this is set to <code>true</code>, message attachments from the incoming exchange and the enricher exchange will be copied to the outgoing message exchange. The default value is <code>false</code> (do not copy message atachments). |
| copyProperties | boolean | If this is set to <code>true</code>, message properties from the incoming exchange and the enricher exchange will be copied to the outgoing message exchange. The default value is <code>false</code> (do not copy message properties). |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| enricherElementName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | returns the QName of the resulting root node |
| enricherTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The target that will receive a copy of the input message and return an addtitional content. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| requestElementName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Returns the QName of the element which contains the 'IN Message' within the response message |
| resultElementName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Returns the QName of the element which contains the message which was produced by the enricherTarget within the response message |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| target | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The target where the enriched exchanges are sent. |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
Eip Resequencer
A resequencer re-orders incoming In-Only or Robust-In-Only exchanges and sends them synchronously to a targets service. Synchronous sending ensures that messages arrive in correct order at the target service. This component implements the Resequencer pattern.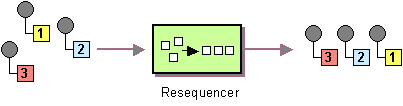
It works on (continuous) streams of message exchanges using a timeout policy. Since the resequencer doesn't make batch reads there's no need to know the number of messages to be re-ordered in advance (although a capacity parameter prevents the resequencer from running out of memory). If the maximum out-of-sequence time difference between messages in a message stream is known, the resequencer's timeout parameter should be set to this value (milliseconds). In this case it is guaranteed that all elements of a stream are delivered in correct order to the target service. The lower the timeout value is compared to the out-of-sequence time difference the higher is the probability for out-of-sequence messages sent by this resequencer. Large timeout values should be supported by sufficiently high capacity values.
For comparing elements of a sequence the resequencer component can be configured with a sequence element comparator. A default comparator is provided that compares message exchanges based on Long sequence numbers. This comparator expects the sequence number to be the value of the org.apache.servicemix.eip.sequence.number property of the exchanges's in\-NormalizedMessage. The name of the property can be customized in the comparator configuration (see below). You may also provide a custom comparator by implementing the SequenceElementComparator interface.
<eip:resequencer
service="sample:Resequencer"
endpoint="ResequencerEndpoint"
comparator="#comparator"
capacity="100"
timeout="2000">
<eip:target>
<eip:exchange-target service="sample:SampleTarget" />
</eip:target>
</eip:resequencer>
<!-- Configure default comparator with custom sequence number property -->
<eip:default-comparator id="comparator" sequenceNumberKey="seqnum"/>
A running example can be downloaded from here. In this example, a custom-coded message sender sends messages in "wrong" order to the resequencer. The resequencer re-orders these messages and (synchronously) sends them to a file sender-endpoint. The file sender-enpoint writes the messages (in proper order) to the work/output directory.
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| capacity | int | The capacity of this resequencer. The capacity determines the maximum number of message that will be kept in memory to put the messages back in sequence. This determine how far two messages can be in the list of messages while still being put back in sequence. |
| comparator | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.resequence.SequenceElementComparator | The comparator used to determine the sequence order of elements. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| target | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | |
| timeout | long | Set the timeout of this resequencer. This specifies the maximum number of milliseconds that can elapse between two out-of-sync messages. |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
Async Bridge
The AsyncBridge expects an InOut mep as input. It then uses the exchange id of the InOut mep as the correlation id and creates an InOnly message by copying the input message and sends it to the target (with the correlation id set as a property). Next it expects an InOnly to come back with the same correlation id property. When this happens, the message is copied to the out message of the original exchange and sent back. If no response is received during the configured amount of time (timeout property in milliseconds), an error will be sent back to the original consumer.
<eip:async-bridge
service="sample:AsyncBridge"
endpoint="AsyncBridgeEndpoint"
<eip:target>
<eip:exchange-target service="sample:SampleTarget" />
</eip:target>
</eip:async-bridge>
Correlation Id
There is a convention between the AsyncBridge and the target on how the correlation id is transmitted. The correlation id can only be transmitted from the AnsycBridge to the target using a message property . The property name can be customized. On the other hand, the correlation id coming back from the target could be set in a message property or the message payload. The AsyncBridge could use an Expression to extract the correlation id from the message returning from the target.
<eip:async-bridge
service="sample:AsyncBridge"
endpoint="AsyncBridgeEndpoint"
responseCorrIdProperty="correlationIdProperty"
responseCorrId="#responseCorrIdExpression">
<eip:target>
<eip:exchange-target service="sample:SampleTarget" />
</eip:target>
</eip:async-bridge>
<bean id="responseCorrIdExpression" class="org.apache.servicemix.expression.JAXPStringXPathExpression" >
<contructor-arg value="/my-response/message/@corrId"/>
</bean>
As you can see from the sample above the responseCorrIdProperty is used to set the name of the property that the target will query to get the correlation id sent by the AsyncBridge. In other words, the target will do something like this to extract the correlation id
String correlationId = exchange.getProperty("correlationIdProperty");
The responseCorrId is set with an instance of type org.apache.servicemix.expression.Expression, in this case the class org.apache.servicemix.expression.JAXPStringXPathExpression.
This expression resolves the location of the correlation id coming back from the target. In the above example the expression shows that the correlation id comes as part of the message payload in an attribute called "corrId" of the /my-response/message element. In a similar manner the class org.apache.servicemix.expression.PropertyExpression could have been used to locate the correlation id in a message property.
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | The lock manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely specified a default implementation will be provided. |
| requestCorrId | org.apache.servicemix.expression.Expression | The expression used to compute the correlation id used to correlate the response and the request. The default behavior is to use the exchange id of the incoming In-Out exchange as the correlation id. |
| responseCorrId | org.apache.servicemix.expression.Expression | The expression used to compute the correlation id from the response exchange. The value computed by this expression must match the one from the {@link #setRequestCorrId} expression. The default value is null, but if no specific expression is configured, an expression will be created which will extract the response correlation id from the {@link #setResponseCorrIdProperty(String)} property on the exchange. |
| responseCorrIdProperty | java.lang.String | Name of the property used by default to compute the correlation id on the response exchange. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure the store to use. If none is explicitely configured, the storeFactory will be used to create one. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | The store factory to use when creating a store. If no factory is explicitely defined, an in-memory only factory will be created. |
| target | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | The target which will be used to send an In-Only or Robust-In-Only exchange to. When receiving an In-Out exchange, the async bridge will create an In-Only request and send it to the specified target. It then expects another In-Only exchange to come back as the response, which will be set as the Out message on the In-Out exchange. This property is mandatory and must be set to a valid target. |
| timeout | long | The timeout property controls the amount of time that the async bridge will wait for the response after having sent the request. The default value is 0 which means that no timeout apply. If set to a non zero value, a timer will be started when after the request is sent. When the timer expires, the In-Out exchange will be sent back with an error status and a {@link java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException} as the cause of the error. The value represents the number of milliseconds to wait. |
| timerManager | org.apache.servicemix.timers.TimerManager | The timer manager to use for this endpoint. If none is explicitely configured, a default implementation will be provided. |
| useRobustInOnly | boolean | Boolean flag to control if In-Only or Robust-In-Only exchange should be used when sending the request. The default value is <code>false</code> which means that an In-Only exchange will be used. When using a Robust-In-Only exchange and when a fault is received, this fault will be sent back to the consumer on the In-Out exchange and the response exchange (if any) would be discarded. For both In-Only and Robust-In-Only, if the request exchange comes back with an Error status, this error will be conveyed back to the consumer in the same way. |
| wsdlExchangeTarget | org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.ExchangeTarget | An exchange target pointing to a JBI endpoint that will be used to load the WSDL describing this endpoint. This can be used when the endpoint proxies another endpoint so that the same WSDL definition will be exposed." |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | When specified, this spring resource will be used to load the WSDL that will be exposed as a description for this endpoint. This property can be used to explicitely define the WSDL to be exposed by this endpoint. This property takes precedence over the wsdlExchangeTarget property. |
Tips
ExchangeTarget
All patterns use the <exchange-target /> tag to specify the target of a JBI exchange.
This element has the following attributes:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| interface | QName | the QName of the target interface. One of service or interface attribute is required |
| operation | QName | the QName of the target operation (optional) |
| service | QName | the QName of the target service. One of service or interface attribute is required |
| endpoint | String | the name of the target JBI endpoint, only used when service is set |
| uri | String | uri used to target the exchange (see URIs) |
NamespaceContext
Some patterns use XPath expression. To use such expressions on an xml with namespaces, you need to define a NamespaceContext.
This NamespaceContext can be referenced by a namespaceContext attribute as shown in the XPathSplitter or MessageFilter examples.
Predicates
Some patterns uses predicates to test a given JBI exchange. The only predicate currently implemented is the XPathPredicate, but you can implement your own and deploy it with the service unit.
Configuring temporary message storage
Many of the pattern implementation need to store MessageExchanges temporarily. An example: the aggregator will need to keep track of the MessageExchange it is aggregating. By default, the EIPs use a plain MemoryStoreFactory to create in-memory stores, but there are other options. If you set the timeout property on the MemoryStoreFactory, it will evict old object from the in-memory store to avoid a memory leak. You can also use a JDBCStoreFactory to store data in a database instead of in memory.
Example: to use an in-memory store with timeout for a storing active and closed aggregations in a <split-aggregator/>, you can do
<eip:split-aggregator service="test:aggregator" endpoint="endpoint"
storeFactory="#StoreFactory" closedAggregateStoreFactory="#StoreFactory">
<eip:target>
<eip:exchange-target service="test:trace5" />
</eip:target>
</eip:split-aggregator>
<bean id="StoreFactory" class="org.apache.servicemix.store.MemoryStoreFactory">
<property name="timeout" value="120000"/> <!-- 2 minute timeout -->
</bean>
Creating your own patterns
Some classes have been designed to be extensible, this includes:
org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.AbstractAggregator
org.apache.servicemix.eip.support.AbstractSplitter
servicemix-exec
Overview
The ServiceMix Exec component is used to invoke commands (executables, binaries, shell commands, shell scripts, etc). The command can be static (defined in the endpoint attributes) or dynamic (provided in the incoming message, including arguments).
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-exec component is http://servicemix.apache.org/exec/1.0. The is an example of <filename>xbean.xml</filename> with a namespace definition with prefix exec.
<beans xmlns:exec="http://servicemix.apache.org/exec/1.0">
<!-- add exec:endpoint definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoints types
The ServiceMix Exec component only defines one endpoint, called exec:endpoint.
Endpoint exec:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | java.lang.String | <p> This attribute specifies the default command to use if no is provided in the incoming message. </p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <code>null</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.exec.marshaler.ExecMarshalerSupport | <p> With this method you can specify a marshaler class which provides the logic for converting a message into a execution command. This class has to implement the interface class <code>ExecMarshalerSupport</code>. If you don't specify a marshaler, the <code>DefaultExecMarshaler</code> will be used. </p> |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| wsdl | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | <p> This attribute specifies the abstract WSDL describing the endpoint behavior. </p> |
Abstract WSDL
TODO
How it works
TODO
servicemix-file
Overview
The ServiceMix File component provides JBI integration to the file system. It can be used to read & write files via URI or to periodically poll directories for new files.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/file/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:file="http://servicemix.apache.org/file/1.0">
<!-- add file:poller and file:sender definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-file component defines two endpoint type:
file:poller :: Periodically polls a directory for files and sends an exchange for every file
file:sender :: Writes the contents of an exchange to a file
file:poller
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| archive | java.io.File | Specifies a directory relative to the polling directory to which processed files are archived. |
| autoCreateDirectory | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint should create the target directory, if it does not already exist. If you set this to <code>false</code> and the directory does not exist, the endpoint will not do anything. Default value is <code>true</code>. |
| comparator | java.util.Comparator | Specifies a <code>Comparator</code> which will be used to sort File listing before starting to process. The default is null, means no sorting. <code>Comparator</code> objects are implementations of <code>java.util.Comparator</code>. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | |
| concurrentPolling | boolean | Sets whether more than one poll can be active at a time (true means yes). Default value is <code>false</code>. |
| delay | long | Sets the amount of time in milliseconds that the endpoint should wait before making the first poll. |
| deleteFile | boolean | Specifies if files should be deleted after they are processed. Default value is <code>true</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| file | java.io.File | Specifies the file or directory to be polled. If it is a directory, all files in the directory or its sub-directories will be processed by the endpoint. If it is a file, only files matching the filename will be processed." |
| filter | java.io.FileFilter | Bean defining the class implementing the file filtering strategy. This bean must be an implementation of the <code>java.io.FileFilter</code> interface. |
| firstTime | java.util.Date | Sets the date on which the first poll will be executed. If a delay is also set using <code>setDelay</code>, the delay interval will be added after the date specified. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | Bean defining the class implementing the file locking strategy. This bean must be an implementation of the <code>org.apache.servicemix.locks.LockManager</code> interface. By default, this will be set to an instances of <code>org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.impl.SimpleLockManager</code>. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler | Specifies a <code>FileMarshaler</code> object that will marshal file data into the NMR. The default file marshaller can read valid XML data. <code>FileMarshaler</code> objects are implementations of <code>org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler</code>. |
| maxConcurrent | int | How many open exchanges can be pending. Default is -1 for unbounded pending exchanges. Set to 1...n to engage throttling of polled file processing. |
| period | long | Sets the number of milliseconds between polling attempts. |
| recursive | boolean | Specifies if sub-directories are polled; if false then the poller will only poll the specified directory. If the endpoint is configured to poll for a specific file rather than a directory then this attribute is ignored. Default is <code>true</code>. |
| scheduler | org.apache.servicemix.common.scheduler.Scheduler | Set a custom Scheduler implementation if you need more fine-grained control over the polling schedule. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| serviceUnit | org.apache.servicemix.common.ServiceUnit | |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
file:sender
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| append | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint appends data to existing files or if it will overwrite existing files. The default is for the endpoint to overwrite existing files. Setting this to <code>true</code> instructs the endpoint to append data. Default value is <code>false</code>. |
| autoCreateDirectory | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint should create the target directory if it does not exist. If you set this to <code>false</code> and the directory does not exist, the endpoint will not do anything. Default value: <code>true</code>. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.file.FileComponent | |
| directory | java.io.File | Specifies the directory where the endpoint writes files. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler | Specifies a <code>FileMarshaler</code> object that will marshal message data from the NMR into a file. The default file marshaler can write valid XML data. <code>FileMarshaler</code> objects are implementations of <code>org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler</code>. |
| overwrite | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint overwrites existing files or not. The default is for the endpoint to not overwrite existing files. Setting this to <code>true</code> instructs the endpoint to overwrite existing files. Default value is <code>false</code>. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| tempFilePrefix | java.lang.String | Specifies a string to prefix to the beginning of generated file names. |
| tempFileSuffix | java.lang.String | Specifies a string to append to generated file names. |
servicemix-ftp
Overview
The ServiceMix FTP component provides JBI integration to the FTP servers. It can be used to read & write files over FTPor to periodically poll directories for new files.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/ftp/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:ftp="http://servicemix.apache.org/ftp/1.0">
<!-- add ftp:poller and ftp:sender definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-ftp component defines two endpoint type:
ftp:poller :: Periodically polls a directory on an FTP server for files and sends an exchange for every file
ftp:sender :: Writes the contents of an exchange to a file on an FTP server
ftp:poller
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| archive | java.net.URI | Specifies a directory relative to the polling directory to which processed files are archived. |
| autoCreateDirectory | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint should create the target directory, if it does not already exist. If you set this to <code>false</code> and the directory does not exist, the endpoint will not do anything. Default value is <code>true</code>. |
| changeWorkingDirectory | boolean | When set to <code>true</code>, the poller will do an explicit <code>cwd</code> into the directory to be polled. Default to <code>false</code>. Recursive polling will not be possible if this feature is enabled. |
| clientPool | org.apache.servicemix.ftp.FTPClientPool | Set a custom FTPClientPool. If this property has not been set, the FTP client pool will be created based on the information provided in the URI. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | the <code>component</code> implementation to use |
| concurrentPolling | boolean | Sets whether more than one poll can be active at a time (true means yes). Default value is <code>false</code>. |
| delay | long | Sets the amount of time in milliseconds that the endpoint should wait before making the first poll. |
| deleteFile | boolean | Delete the file after it has been succesfully processed? Defaults to <code>true</code> |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| filter | java.io.FileFilter | Sets the filter to select which files have to be processed. When not set, all files will be picked up by the poller. |
| firstTime | java.util.Date | Sets the date on which the first poll will be executed. If a delay is also set using <code>setDelay</code>, the delay interval will be added after the date specified. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | Set a custom LockManager implementation for keeping track of which files are already being processed. The default implementation is a simple, in-memory lock management system. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler | Set a custom FileMarshaler implementation to control how the file contents is being translated into a JBI message. The default implementation reads XML contents from the file. |
| period | long | Sets the number of milliseconds between polling attempts. |
| recursive | boolean | Specifies whether subdirectories should be polled. Defaults to <code>true</code> |
| scheduler | org.apache.servicemix.common.scheduler.Scheduler | Set a custom Scheduler implementation if you need more fine-grained control over the polling schedule. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| serviceUnit | org.apache.servicemix.common.ServiceUnit | |
| stateless | boolean | When set to <code>false</code> |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Set the operation to be invoked on the target service. |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
| uri | java.net.URI | Configures the endpoint from a URI. |
ftp:sender
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| autoCreateDirectory | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint should create the target directory, if it does not already exist. If you set this to <code>false</code> and the directory does not exist, the endpoint will not do anything. Default value is <code>true</code>. |
| checkDuplicates | boolean | Specifies whether duplicates should be checked. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| clientPool | org.apache.servicemix.ftp.FTPClientPool | Set a custom FTPClientPool. If this property has not been set, the FTP client pool will be created based on the information provided in the URI. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.ftp.FtpComponent | |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler | Set a custom FileMarshaler implementation to control how the file contents is being translated into a JBI message. The default implementation reads XML contents from the file. |
| overwrite | boolean | Specifies if a file with the same name already exists on the FTP server, the file should be overwritten. Defaults to <code>false</code>. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| uniqueFileName | java.lang.String | Sets the name used to make a unique name if no file name is available on the message. |
| uploadPrefix | java.lang.String | Set the file name prefix used during upload. The prefix will be automatically removed as soon as the upload has completed. This allows other processes to discern completed files from files that are being uploaded. |
| uploadSuffix | java.lang.String | Set the file name suffix used during upload. The suffix will be automatically removed as soon as the upload has completed. This allows other processes to discern completed files from files that are being uploaded. |
| uri | java.net.URI | Configures the endpoint from a URI |
Examples
Using ftp:pool to configure the FTP connections
In order to gain more control over the FTP connection parameters (active/passive, timeout, ...) that are being used, you can define your own FTP connection pool. Afterward, you can refer to the pool object from both a sender and poller endpoint.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<beans xmlns:ftp="http://servicemix.apache.org/ftp/1.0"
xmlns:sample="urn:servicemix:example">
<ftp:sender service="sample:sender" endpoint="endpoint"
uri="ftp://localhost/myfolder"
clientPool="#clientPool"/>
<ftp:pool id="clientPool" username="myname" password="$ecret"
dataTimeout="90000" />
</beans>
The table below shows the full list of options offered by ftp:pool:
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| address | java.net.InetAddress | Set the remote internet address to connect to. |
| binaryMode | boolean | Use binary mode transfers. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| config | org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClientConfig | Configure a custom FTPClientConfig instance to allow more fine-grained control over the FTP connections in the pool. |
| controlEncoding | java.lang.String | Configure the encoding used in the FTP control connections. Defaults to <code>ISO-8859-1</code> |
| dataTimeout | int | Specifies a timeout used on the FTP data connection. Defaults to <code>120000</code> |
| host | java.lang.String | Set the remote host name to connect to. |
| localAddress | java.net.InetAddress | Set the local IP address to be used when establishing the connection. |
| localPort | int | Set the local TCP/IP port to be used when establishing the connection. |
| passiveMode | boolean | Use passive mode FTP transfers. Defaults to <code>false</code> |
| password | java.lang.String | Set the password for logging into the FTP server. |
| pool | org.apache.commons.pool.ObjectPool | Set a custom ObjectPool instance to use for the connection pooling. |
| port | int | Set the remote port number to connect to. |
| username | java.lang.String | Set the login to use to access the FTP server. |
If you need even more fine-grained control over the FTP connections or the way the payloads are being handled, have a look at the Camel FTP component, which offers a lot of options out of the box, but also allows setting any property on its underlying Commons NET FTPClient and FTPClientConfig instances.
servicemix-http
Overview
ServiceMix ships with a JBI compliant HTTP/SOAP binding component named servicemix-http.
Here are the main features:
JBI compliant Binding Component
Usable in a lightweight mode in servicemix.xml configuration files
Integrated HTTP server based on Jetty 6
HTTP Client using Jakarta Commons HTTP Client
Highly performant and scalable using Jetty 6 continuations
SOAP 1.1 and 1.2 support
MIME attachments
WS-Addressing support
WSDL based and XBean based deployments
Support for all MEPs as consumers or providers
SSL support
WS-Security support
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/http/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:http="http://servicemix.apache.org/http/1.0">
<!-- add http:consumer, http:soap-consumer
http:provider and http soap:provider definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-http component defines four endpoint type:
http:consumer :: This endpoint allows you to expose a service in the ESB to the outside world over HTTP. Whenever it receives an HTTP request, it will interact with the configured services on the ESB to provide the HTTP response.
http:soap-consumer :: Similar to http:consumer, but specifically geared towards handing SOAP requests and responses
http:provider :: This endpoint allows you to access remote services from within the ESB. It will perform an external HTTP request whenever it receives a JBI MessageExchange
http:soap-provider :: Similar to http:provider, but specifically geared towards performing SOAP requests
It also provides one additional legacy endpoints, which are still available to ease migration from ServiceMix 3:
http:endpoint :: (Deprecated) Legacy endpoint, capable to acting as a consumer or provider based on the configuration
http:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| authMethod | java.lang.String | a string naming the scheme used for authenticating users |
| basicAuthentication | org.apache.servicemix.http.BasicAuthCredentials | authentication data for using basic HTTP authentication. |
| binding | javax.wsdl.extensions.ExtensibilityElement | |
| defaultMep | java.net.URI | |
| defaultOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | |
| description | org.w3c.dom.Document | |
| dynamic | boolean | |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| locationURI | java.lang.String | the URI to which a provider endpoint sends requests |
| policies | (java.lang.Object)\* | |
| proxy | org.apache.servicemix.http.ProxyParameters | configuration used to establish a proxy for sending HTTP requests. This configuration overrides that which is set at the component level. |
| responseContentTypeCheck | boolean | Specifies if the http provider checks the response content type for the |
| role | java.lang.String | HTTP endpoints can be either consumers or providers. Specifying |
| roleAsString | java.lang.String | |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| soap | boolean | |
| soapAction | java.lang.String | |
| soapVersion | java.lang.String | |
| ssl | org.apache.servicemix.http.SslParameters | a bean containing the SSL configuration properties |
| synchronous | boolean | |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | |
| targetInterfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | |
| timeout | int | the number of milliseconds before the endpoint times out. The default value is 0 which means that the endpoint will never timeout. |
| wantContentTypeHeaderFromExchangeIntoHttpRequest | boolean | Specifies if the HTTP provider will copy the HTTP request headers into the JBI |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource |
http:consumer
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| authMethod | java.lang.String | a string naming the scheme used for authenticating users |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | |
| defaultMep | java.net.URI | a URI representing the endpoint's default MEP. The default is |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| locationURI | java.lang.String | the URI at which the endpoint listens for requests |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.http.endpoints.HttpConsumerMarshaler | the bean used to marshal HTTP messages. The default is a |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| serviceUnit | org.apache.servicemix.common.ServiceUnit | |
| ssl | org.apache.servicemix.http.SslParameters | a bean containing the SSL configuration properties |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
| timeout | long | the timeout is specified in milliseconds. The default value is 0 which |
http:provider
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| clientSoTimeout | int | the number of milliseconds the endpoint will block while attempting to read a request. The default value is 60000. Setting this to 0 specifies that the endpoint will never timeout. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | |
| credentials | java.lang.String | The authentication credentials |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| expectGzippedResponse | boolean | If true, the accept-encoding http header will be set to gzip and the response will be un-gzipped. |
| gzipRequest | boolean | If true, the request content will be gzipped and sent over the wire. The content-encoding http header will also be set to gzip. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| locationURI | java.lang.String | the URI to which the endpoint sends requests |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.http.endpoints.HttpProviderMarshaler | the bean used to marshal HTTP messages. The default is a |
| principal | java.lang.String | The authentication principal |
| providerExpirationTime | int | the number of milliseconds to wait for a response before expiring. |
| proxyHost | java.lang.String | the host name of the HTTP proxy |
| proxyPassword | java.lang.String | the password for the HTTP proxy authentication |
| proxyPort | int | the host port of the HTTP proxy (defaults to 80) |
| proxyUsername | java.lang.String | the user name for the HTTP proxy authentication |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| serviceUnit | org.apache.servicemix.common.ServiceUnit | |
| ssl | org.apache.servicemix.http.SslParameters | the SSL parameters |
http:soap-consumer
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| authMethod | java.lang.String | a string naming the scheme used for authenticating users |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | |
| defaultMep | java.net.URI | a URI representing the endpoint's default MEP. The default is |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| locationURI | java.lang.String | the URI at which the endpoint listens for requests |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.http.endpoints.HttpConsumerMarshaler | the bean used to marshal HTTP messages. The default is a |
| policies | (org.apache.servicemix.soap.api.Policy)\* | a list of interceptors that will process messages |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| serviceUnit | org.apache.servicemix.common.ServiceUnit | |
| soapVersion | java.lang.String | Specifies the SOAP version to use when generating a wsdl binding for |
| ssl | org.apache.servicemix.http.SslParameters | a bean containing the SSL configuration properties |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
| timeout | long | the timeout is specified in milliseconds. The default value is 0 which |
| useJbiWrapper | boolean | Specifies if the JBI wrapper is sent in the body of the message. Default is |
| validateWsdl | boolean | Specifies if the WSDL is checked for WSI-BP compliance. Default is <code>true</code>. |
| wsdl | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | the URL of the WSDL document defining the endpoint's messages |
http:soap-provider
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| clientSoTimeout | int | the number of milliseconds the endpoint will block while attempting to read a request. The default value is 60000. Setting this to 0 specifies that the endpoint will never timeout. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | |
| credentials | java.lang.String | The authentication credentials |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| expectGzippedResponse | boolean | If true, the accept-encoding http header will be set to gzip and the response will be un-gzipped. |
| gzipRequest | boolean | If true, the request content will be gzipped and sent over the wire. The content-encoding http header will also be set to gzip. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| locationURI | java.lang.String | the URI to which the endpoint sends requests |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.http.endpoints.HttpProviderMarshaler | the bean used to marshal HTTP messages. The default is a |
| policies | (org.apache.servicemix.soap.api.Policy)\* | a list of interceptors that will process messages |
| principal | java.lang.String | The authentication principal |
| providerExpirationTime | int | the number of milliseconds to wait for a response before expiring. |
| proxyHost | java.lang.String | the host name of the HTTP proxy |
| proxyPassword | java.lang.String | the password for the HTTP proxy authentication |
| proxyPort | int | the host port of the HTTP proxy (defaults to 80) |
| proxyUsername | java.lang.String | the user name for the HTTP proxy authentication |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| serviceUnit | org.apache.servicemix.common.ServiceUnit | |
| ssl | org.apache.servicemix.http.SslParameters | the SSL parameters |
| useJbiWrapper | boolean | Specifies if the JBI wrapper is sent in the body of the message. Default is |
| validateWsdl | boolean | Specifies if the WSDL is checked for WSI-BP compliance. Default is <code>true</code> |
| wsdl | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | the URL of the WSDL document defining the endpoint's messages |
servicemix-jms
Overview
ServiceMix ships with a JBI compliant JMS binding component named servicemix-jms.
Here are the main features:
JBI compliant Binding Component
Usable in a lightweight mode in servicemix.xml configuration files
SOAP 1.1 and 1.2 support
MIME attachments
WS-Addressing support
WSDL based and XBean based deployments
Support for all MEPs as consumers or providers
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/jms/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:jms="http://servicemix.apache.org/jms/1.0">
<!-- add jms:consumer, jms:soap-consumer, jms:jca-consumer,
jms:provider, jms:soap-provider and jms:jca-provider definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-jms component defines six endpoint type:
jms:consumer :: This endpoint allows you to expose a service in the ESB to the outside world over JMS. Whenever it receives a JMS message, it will interact with the configured services on the ESB.
jms:soap-consumer :: Similar to jms:consumer, but specifically geared towards handing SOAP requests and responses
jms:jca-consumer :: Similar to jms:consumer, but adds the possibility of using a JCA resource adapter
jms:provider :: This endpoint allows you to access remote services from within the ESB. It will send a JMS message whenever it receives a JBI MessageExchange
jms:soap-provider :: Similar to jms:provider, but specifically geared towards performing SOAP requests
jms:jca-provider :: Similar to jms:provider, but adds the possibility of using a JCA resource adapter
It also provides one additional legacy endpoints, which are still available to ease migration from ServiceMix 3:
jms:endpoint :: (Deprecated) Legacy endpoint, capable to acting as a consumer or provider based on the configuration
jms:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| activationSpec | javax.resource.spi.ActivationSpec | The ActivationSpec to use on a JCA consumer endpoint. |
| bootstrapContext | javax.resource.spi.BootstrapContext | The BootstrapContext to use for a JCA consumer endpoint. |
| connectionFactory | javax.jms.ConnectionFactory | A configured ConnectionFactory to use on this endpoint. |
| defaultMep | java.net.URI | |
| defaultOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | |
| description | org.w3c.dom.Document | |
| destination | javax.jms.Destination | A configured Destination to use on this endpoint. |
| destinationStyle | java.lang.String | Specifies the destination type used with the jmsProviderDestinationName. Can be <code>queue</code> or <code>topic</code>. |
| dynamic | boolean | |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| initialContextFactory | java.lang.String | The class name of the JNDI InitialContextFactory to use. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| jmsProviderDestinationName | java.lang.String | The name of the destination created by a call to <code>Session.createQueue</code> or <code>Session.createTopic</code>. This property is used when <code>destination</code> and <code>jndiDestinationName</code> are both <code>null</code>. |
| jmsProviderReplyToName | java.lang.String | The name of the reply destination created by a call to <code>Session.createQueue</code> or <code>Session.createTopic</code>. This property is used when <code>jndiReplyToName</code> is <code>null</code>. A temporary queue will be used if a replyTo is not provided. |
| jndiConnectionFactoryName | java.lang.String | The name of the JMS ConnectionFactory to lookup in JNDI. Used if <code>connectionFactory</code> is <code>null</code> |
| jndiDestinationName | java.lang.String | The name of the JMS Destination to lookup in JNDI. Used if <code>destination</code> is <code>null</code>. |
| jndiProviderURL | java.lang.String | The provider URL used to create the JNDI context. |
| jndiReplyToName | java.lang.String | The name of the JMS Reply-to destination to lookup in JNDI. If this property is not set a temporary replyTo queue is used. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.jms.JmsMarshaler | Specifies the class implementing the logic for marshaling and unmarshaling messages between the JMS destination and the endpoint. Defaults to <code>DefaultJmsMarshaler</code>. |
| needJavaIdentifiers | boolean | Indicates if the JMS properties used by the endpoint need to be spec compliant. |
| policies | (java.lang.Object)\* | |
| processorName | java.lang.String | Specifies the processor family to use for this endpoint. Can be: <ul> <li><code>multiplexing</code> (default)</li> <li><code>standard</code></li> <li><code>jca</code></li> </ul> |
| resourceAdapter | javax.resource.spi.ResourceAdapter | The ResourceAdapter to use on a JCA consumer endpoint. |
| role | java.lang.String | Specifies the role of this endpoint. Endpoints can be <code>consumer</code> or <code>provider</code>. |
| roleAsString | java.lang.String | |
| rollbackOnError | boolean | Indicates if the JBI exchange is rolled back if an error is encountered. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| soap | boolean | |
| soapVersion | java.lang.String | |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Specifies a persistent data store to hold pending exchanges for the endpoint. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | Specifies the factory used to create presistent data stores for this endpoint. |
| synchronous | boolean | Indicates if a JCA consumer endpoint sends the JBI exchange synchronously or asynchronously. This changes the transaction boundary. |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | |
| targetInterfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | |
| useMsgIdInResponse | boolean | Indicates whether the message id of the request message should be used as the correlation id in the response or the correlation id of the request. |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource |
jms:consumer
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cacheLevel | int | Specifies the level of caching allowed by the listener. Valid values are 0 through 3. The values map to the following: <ul> <li>0 - <code>CACHE_NONE</code></li> <li>1 - <code>CACHE_CONNECTION</code></li> <li>2 - <code>CACHE_SESSION</code></li> <li>3 - <code>CACHE_CONSUMER</code></li> </ul> The default is <code>CACHE_NONE</code>.<br/> This property only effects consumers whose <code>listenerType</code> property is set to <code>default</code>. |
| clientId | java.lang.String | Specifies the JMS client id for a shared <code>Connection</code> created and used by this listener. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | |
| concurrentConsumers | int | Specifies the number of concurrent consumers created by the listener. This property is only used for consumers whose <code>listenerType</code> property is set to either <code>simple</code> or <code>default</code>. |
| connectionFactory | javax.jms.ConnectionFactory | Specifies the <code>ConnectionFactory</code> used by the endpoint. |
| destination | javax.jms.Destination | Specifies the JMS <code>Destination</code> used to receive messages. |
| destinationChooser | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.DestinationChooser | Specifies a class implementing logic for choosing reply destinations. |
| destinationName | java.lang.String | Specifies a string identifying the JMS destination used to recieve messages. The destination is resolved using the <code>DesitinationResolver</code>. |
| destinationResolver | org.springframework.jms.support.destination.DestinationResolver | Specifies the class implementing logic for converting strings into destinations. The default is <code>DynamicDestinationResolver</code>. |
| durableSubscriptionName | java.lang.String | Specifies the name used to register the durable subscription. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| exceptionListener | javax.jms.ExceptionListener | Specifies an <code>ExceptionListener</code> to notify in case of a <code>JMSException</code> is thrown by the registered message listener or the invocation infrastructure. |
| idleTaskExecutionLimit | int | Specifies the limit for idle executions of a receive task, not having received any message within its execution. If this limit is reached, the task will shut down and leave receiving to other executing tasks (in case of dynamic scheduling; see the "maxConcurrentConsumers" setting). Within each task execution, a number of message reception attempts (according to the "maxMessagesPerTask" setting) will each wait for an incoming message (according to the "receiveTimeout" setting). If all of those receive attempts in a given task return without a message, the task is considered idle with respect to received messages. Such a task may still be rescheduled; however, once it reached the specified "idleTaskExecutionLimit", it will shut down (in case of dynamic scaling). Raise this limit if you encounter too frequent scaling up and down. With this limit being higher, an idle consumer will be kept around longer, avoiding the restart of a consumer once a new load of messages comes in. Alternatively, specify a higher "maxMessagePerTask" and/or "receiveTimeout" value, which will also lead to idle consumers being kept around for a longer time (while also increasing the average execution time of each scheduled task). |
jms:provider
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connectionFactory | javax.jms.ConnectionFactory | Specifies the <code>ConnectionFactory</code> used by the endpoint. |
| deliveryMode | int | Specifies the JMS delivery mode used for the reply. Defaults to (2)(<code>PERSISTENT</code>). |
| destination | javax.jms.Destination | Specifies the JMS <code>Destination</code> used to send messages. |
| destinationChooser | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.DestinationChooser | Specifies a class implementing logic for choosing the destination used to send messages. |
| destinationName | java.lang.String | Specifies a string identifying the JMS destination used to send messages. The destination is resolved using the <code>DesitinationResolver</code>. |
| destinationResolver | org.springframework.jms.support.destination.DestinationResolver | Specifies the class implementing logic for converting strings into destinations. The default is <code>DynamicDestinationResolver</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| explicitQosEnabled | boolean | Specifies if the QoS values specified for the endpoint are explicitly used when a messages is sent. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| jms102 | boolean | Determines if the provider used JMS 1.0.2 compliant APIs. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.JmsProviderMarshaler | Specifies the class implementing the message marshaler. The message marshaller is responsible for marshalling and unmarshalling JMS messages. The default is <code>DefaultProviderMarshaler</code>. |
| messageIdEnabled | boolean | Specifies if your endpoint requires JMS message IDs. Setting the <code>messageIdEnabled</code> property to <code>false</code> causes the endpoint to call its message producer's <code>setDisableMessageID() </code> with a value of <code>true</code>. The JMS broker is then given a hint that it does not need to generate message IDs or add them to the messages from the endpoint. The JMS broker can choose to accept the hint or ignore it. |
| messageTimestampEnabled | boolean | Specifies if your endpoints requires time stamps on its messages. Setting the <code>messageTimeStampEnabled</code> property to <code>false</code> causes the endpoint to call its message producer's <code>setDisableMessageTimestamp() </code> method with a value of <code>true</code>. The JMS broker is then given a hint that it does not need to generate message IDs or add them to the messages from the endpoint. The JMS broker can choose to accept the hint or ignore it. |
| preserveMessageQos | boolean | Specifies whether we want to send message using the QoS settings specified on the message instead in order to preserve message QoS. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| priority | int | Specifies the priority assigned to the JMS messages. Defaults to 4. |
| pubSubDomain | boolean | Specifies if the destination is a topic. <code>true</code> means the destination is a topic. <code>false</code> means the destination is a queue. |
| pubSubNoLocal | boolean | Specifies if messages published by the listener's <code>Connection</code> are suppressed. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| receiveTimeout | long | Specifies the timeout for receiving a message in milliseconds. |
| replyDestination | javax.jms.Destination | Sets the reply destination. This JMS destination will be used as the default destination for the response messages when using an InOut JBI exchange. It will be used if the <code>replyDestinationChooser</code> does not return any value. |
| replyDestinationChooser | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.DestinationChooser | Specifies a class implementing logic for choosing the destination used to recieve replies. |
| replyDestinationName | java.lang.String | Sets the name of the reply destination. This property will be used to create the <code>replyDestination</code> using the <code>destinationResolver</code> when the endpoint starts if the <code>replyDestination</code> has not been set. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Sets the store used to store JBI exchanges that are waiting for a response JMS message. The store will be automatically created if not set. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | Sets the store factory used to create the store. If none is set, a {@link MemoryStoreFactory} will be created and used instead. |
| timeToLive | long | Specifies the number of milliseconds a message is valid. |
jms:soap-consumer
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cacheLevel | int | Specifies the level of caching allowed by the listener. Valid values are 0 through 3. The values map to the following: <ul> <li>0 - <code>CACHE_NONE</code></li> <li>1 - <code>CACHE_CONNECTION</code></li> <li>2 - <code>CACHE_SESSION</code></li> <li>3 - <code>CACHE_CONSUMER</code></li> </ul> The default is <code>CACHE_NONE</code>.<br/> This property only effects consumers whose <code>listenerType</code> property is set to <code>default</code>. |
| clientId | java.lang.String | Specifies the JMS client id for a shared <code>Connection</code> created and used by this listener. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | |
| concurrentConsumers | int | Specifies the number of concurrent consumers created by the listener. This property is only used for consumers whose <code>listenerType</code> property is set to either <code>simple</code> or <code>default</code>. |
| connectionFactory | javax.jms.ConnectionFactory | Specifies the <code>ConnectionFactory</code> used by the endpoint. |
| destination | javax.jms.Destination | Specifies the JMS <code>Destination</code> used to receive messages. |
| destinationChooser | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.DestinationChooser | Specifies a class implementing logic for choosing reply destinations. |
| destinationName | java.lang.String | Specifies a string identifying the JMS destination used to recieve messages. The destination is resolved using the <code>DesitinationResolver</code>. |
| destinationResolver | org.springframework.jms.support.destination.DestinationResolver | Specifies the class implementing logic for converting strings into destinations. The default is <code>DynamicDestinationResolver</code>. |
| durableSubscriptionName | java.lang.String | Specifies the name used to register the durable subscription. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| exceptionListener | javax.jms.ExceptionListener | Specifies an <code>ExceptionListener</code> to notify in case of a <code>JMSException</code> is thrown by the registered message listener or the invocation infrastructure. |
| idleTaskExecutionLimit | int | Specifies the limit for idle executions of a receive task, not having received any message within its execution. If this limit is reached, the task will shut down and leave receiving to other executing tasks (in case of dynamic scheduling; see the "maxConcurrentConsumers" setting). Within each task execution, a number of message reception attempts (according to the "maxMessagesPerTask" setting) will each wait for an incoming message (according to the "receiveTimeout" setting). If all of those receive attempts in a given task return without a message, the task is considered idle with respect to received messages. Such a task may still be rescheduled; however, once it reached the specified "idleTaskExecutionLimit", it will shut down (in case of dynamic scaling). Raise this limit if you encounter too frequent scaling up and down. With this limit being higher, an idle consumer will be kept around longer, avoiding the restart of a consumer once a new load of messages comes in. Alternatively, specify a higher "maxMessagePerTask" and/or "receiveTimeout" value, which will also lead to idle consumers being kept around for a longer time (while also increasing the average execution time of each scheduled task). |
jms:soap-provider
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connectionFactory | javax.jms.ConnectionFactory | Specifies the <code>ConnectionFactory</code> used by the endpoint. |
| deliveryMode | int | Specifies the JMS delivery mode used for the reply. Defaults to (2)(<code>PERSISTENT</code>). |
| destination | javax.jms.Destination | Specifies the JMS <code>Destination</code> used to send messages. |
| destinationChooser | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.DestinationChooser | Specifies a class implementing logic for choosing the destination used to send messages. |
| destinationName | java.lang.String | Specifies a string identifying the JMS destination used to send messages. The destination is resolved using the <code>DesitinationResolver</code>. |
| destinationResolver | org.springframework.jms.support.destination.DestinationResolver | Specifies the class implementing logic for converting strings into destinations. The default is <code>DynamicDestinationResolver</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| explicitQosEnabled | boolean | Specifies if the QoS values specified for the endpoint are explicitly used when a messages is sent. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| jms102 | boolean | Determines if the provider used JMS 1.0.2 compliant APIs. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.JmsProviderMarshaler | Specifies the class implementing the message marshaler. The message marshaller is responsible for marshalling and unmarshalling JMS messages. The default is <code>DefaultProviderMarshaler</code>. |
| messageIdEnabled | boolean | Specifies if your endpoint requires JMS message IDs. Setting the <code>messageIdEnabled</code> property to <code>false</code> causes the endpoint to call its message producer's <code>setDisableMessageID() </code> with a value of <code>true</code>. The JMS broker is then given a hint that it does not need to generate message IDs or add them to the messages from the endpoint. The JMS broker can choose to accept the hint or ignore it. |
| messageTimestampEnabled | boolean | Specifies if your endpoints requires time stamps on its messages. Setting the <code>messageTimeStampEnabled</code> property to <code>false</code> causes the endpoint to call its message producer's <code>setDisableMessageTimestamp() </code> method with a value of <code>true</code>. The JMS broker is then given a hint that it does not need to generate message IDs or add them to the messages from the endpoint. The JMS broker can choose to accept the hint or ignore it. |
| policies | (org.apache.servicemix.soap.api.Policy)\* | Specifies an array of interceptors used to process SOAP messages. |
| preserveMessageQos | boolean | Specifies whether we want to send message using the QoS settings specified on the message instead in order to preserve message QoS. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| priority | int | Specifies the priority assigned to the JMS messages. Defaults to 4. |
| pubSubDomain | boolean | Specifies if the destination is a topic. <code>true</code> means the destination is a topic. <code>false</code> means the destination is a queue. |
| pubSubNoLocal | boolean | Specifies if messages published by the listener's <code>Connection</code> are suppressed. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| receiveTimeout | long | Specifies the timeout for receiving a message in milliseconds. |
| replyDestination | javax.jms.Destination | Sets the reply destination. This JMS destination will be used as the default destination for the response messages when using an InOut JBI exchange. It will be used if the <code>replyDestinationChooser</code> does not return any value. |
| replyDestinationChooser | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.DestinationChooser | Specifies a class implementing logic for choosing the destination used to recieve replies. |
| replyDestinationName | java.lang.String | Sets the name of the reply destination. This property will be used to create the <code>replyDestination</code> using the <code>destinationResolver</code> when the endpoint starts if the <code>replyDestination</code> has not been set. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Sets the store used to store JBI exchanges that are waiting for a response JMS message. The store will be automatically created if not set. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | Sets the store factory used to create the store. If none is set, a {@link MemoryStoreFactory} will be created and used instead. |
| timeToLive | long | Specifies the number of milliseconds a message is valid. |
| useJbiWrapper | boolean | Specifies if the endpoint expects SOAP messages to be wrapped in the JBI wrapper. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| validateWsdl | boolean | Specifies if the WSDL is checked WSI-BP compliance. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| wsdl | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Specifies the WSDL document describing the service's interface. |
jms:jca-consumer
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| activationSpec | javax.resource.spi.ActivationSpec | Specifies the activation information needed by the endpoint. |
| bootstrapContext | javax.resource.spi.BootstrapContext | Specifies the <code>BootStrapContext</code> used to start the resource adapter. If this property is not set, a default <code>BootstrpContext</code> will be created. |
| connectionFactory | javax.jms.ConnectionFactory | Specifies the <code>ConnectionFactory</code> used by the endpoint. |
| destinationChooser | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.DestinationChooser | Specifies a class implementing logic for choosing reply destinations. |
| destinationResolver | org.springframework.jms.support.destination.DestinationResolver | Specifies the class implementing logic for converting strings into destinations. The default is <code>DynamicDestinationResolver</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| jms102 | boolean | Specifies if the consumer uses JMS 1.0.2 compliant APIs. Defaults to <code>false</code>. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.jms.endpoints.JmsConsumerMarshaler | Specifies the class implementing the message marshaler. The message marshaller is responsible for marshalling and unmarshalling JMS messages. The default is <code>DefaultConsumerMarshaler</code>. |
| pubSubDomain | boolean | Specifies if the destination is a topic. <code>true</code> means the destination is a topic. <code>false</code> means the destination is a queue. |
| replyDeliveryMode | int | Specifies the JMS delivery mode used for the reply. Defaults to 2(<code>PERSISTENT</code>). |
| replyDestination | javax.jms.Destination | Specifies the JMS <code>Destination</code> for the replies. If this value is not set the endpoint will use the <code>destinationChooser</code> property or the <code>replyDestinationName</code> property to determine the desitination to use. |
| replyDestinationName | java.lang.String | Specifies the name of the JMS destination to use for the reply. The actual JMS destination is resolved using the <code>DestinationResolver</code> specified by the <code>.destinationResolver</code> property. |
| replyExplicitQosEnabled | boolean | Specifies if the QoS values specified for the endpoint are explicitly used when the reply is sent. The default is <code>false</code>. |
| replyPriority | int | Specifies the JMS message priority of the reply. Defaults to 4. |
| replyProperties | java.util.Map | Specifies custom properties to be placed in the reply's JMS header. |
| replyTimeToLive | long | Specifies the number of milliseconds the reply message is valid. The default is unlimited. |
| resourceAdapter | javax.resource.spi.ResourceAdapter | Specifies the resource adapter used for the endpoint. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| stateless | boolean | Specifies if the consumer retains state information about the message exchange while it is in process. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Specifies the persistent store used to store JBI exchanges that are waiting to be processed. The store will be automatically created if not set and the endpoint's <code>stateless</code> property is set to <code>false</code>. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | Specifies the store factory used to create the store. If none is set and the endpoint's <code>stateless</code> property is set to <code>false</code>, a {@link MemoryStoreFactory} will be created and used instead. |
| synchronous | boolean | Specifies if the consumer will block while waiting for a response. This means the consumer can only process one message at a time. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
| useMessageIdInResponse | java.lang.Boolean | Specifies if the request message's ID is used as the reply's correlation ID. The default behavior is to use the request's correlation ID. Setting this to <code>true</code> means the request's message ID will be used instead. |
servicemix-mail
Overview
he ServiceMix Mail component provides support for receiving and sending mails via the enterprise service bus.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/mail/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:mail="http://servicemix.apache.org/mail/1.0">
<!-- add mail:poller and mail:sender definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-mail component defines two endpoint type:
mail:poller :: Connect to a POP3 or IMAP server and send a MessageExchange for every mail
mail:sender :: Connect to an SMTP server and send a mail for every JBI MessageExchange it receives
mail:poller
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| concurrentPolling | boolean | Sets whether more than one poll can be active at a time (true means yes). Default value is <code>false</code>. |
| connection | java.lang.String | <p>Specifies the connection URI used to connect to a mail server. <br /><br /> <b><u>Templates:</u></b> <br /> nbsp; i><rotocol>//<ser><ost>:<ort>/<older>?password=<assword>/i> <br /><b> nbsp; nbsp; nbsp;OR</b><br/> nbsp; i><rotocol>//<ost>:<ort>/<older>?user=<ser>password=<assword>/i> <br /><br /> <b><u>Details:</u></b><br /><br/> <table border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"> <tr> <td width="40%" align="left"><b><u>Name</u></b></td> <td width="60%" align="left"><b><u>Description</u></b></td> </tr> <tr> <td>protocol</td> <td>the protocol to use (example: pop3 or imap)</td> </tr> <tr> <td>user</td> <td>the user name used to log into an account</td> </tr> <tr> <td>host</td> <td>the name or ip address of the mail server</td> </tr> <tr> <td>port</td> <td>the port number to use (optional)</td> </tr> <tr> <td>folder</td> <td>the folder to poll from (optional)</td> </tr> <tr> <td>password</td> <td>the password for the login</td> </tr> </table> <br/> <b><u>Examples:</u></b><br /> nbsp; i>imap://lhein@imapserver:143/INBOX?password=mypass</i><br /> nbsp; i>pop3://pop3server/INBOX?user=me@myhome.org;password=mypass</i></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| customProperties | java.util.Map | <p>Specifies a <code>java.util.Map</code> which may contain additional properties for the connection. <br/> <br/><b><u>Example for disabling TOP for POP3 headers:</u></b><br /> i><b>key</b>: "mail.pop3.disabletop"</i> <br /> i><b>value</b>: "true"</i></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| customTrustManagers | java.lang.String | <p>Specifies one or more trust manager classes separated by a semicolon (<b>;</b>).<br/> These classes have to implement the <code>Trustmanager</code> interface and need to provide an empty default constructor to be valid.<br/><br /> If you want to accept all security certificates without a check you may consider using the <code>DummyTrustManager</code> class. It is actually only an empty stub without any checking logic. <br/><b>But be aware that this will be a security risk in production environments. </b></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| debugMode | boolean | <p>Specifies if the JavaMail is run in <code>DEBUG</code> mode. This means that while connecting to server and processing mails a detailed log is written to debug output. <br /> This mode is very handy if you are experiencing problems with your mail server connection and you want to find out what is going wrong in communication with the server. <br /><br /> nbsp; b>true</b> - <i>the debug mode is <b>enabled</b></i> <br /> nbsp; b>false</b> - <i>the debug mode is <b>disabled</b></i></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>false</b></i><br/><br/> |
| delay | long | Sets the amount of time in milliseconds that the endpoint should wait before making the first poll. |
| deleteProcessedMessages | boolean | <p>This flag is used to indicate what happens to a processed mail polled from a mail folder. If it is set to <code>true</code> the mail will be deleted after it was sent into the bus successfully. If set to <code>false</code> the mail will reside inside the mail folder but will be marked as already seen.<br/> If the sending of the mail results in an error, the mail will not be deleted / marked and reprocessed on next run of the polling cycle.<p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>false</b></i> |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| firstTime | java.util.Date | Sets the date on which the first poll will be executed. If a delay is also set using <code>setDelay</code>, the delay interval will be added after the date specified. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.mail.marshaler.AbstractMailMarshaler | <p>With this method you can specify a marshaler class which provides the logic for converting a mail into a normalized message. This class has to extend the abstract class <code>AbstractMailMarshaler</code> or an extending class. If you don't specify a marshaler, the <code>DefaultMailMarshaler</code> will be used.</p> |
| maxFetchSize | int | <p>This sets the maximum amount of mails to process within one polling cycle. If the maximum amount is reached all other mails in "unseen" state will be skipped.</p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>-1 (unlimited)</b></i><br/><br/> |
| period | long | Sets the number of milliseconds between polling attempts. |
| processOnlyUnseenMessages | boolean | <p>This flag is used to indicate whether all mails are polled from a mail folder or only the unseen mails are processed.<br/><br /> If it is set to <b><code>true</code></b> only the unseen mails will be processed.<br /> If it is set to <b><code>false</code></b> all mails will be processed.<br/></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>true</b></i><br/><br/> |
| scheduler | org.apache.servicemix.common.scheduler.Scheduler | Set a custom Scheduler implementation if you need more fine-grained control over the polling schedule. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| storage | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | <p>Specifies a <code>org.apache.servicemix.store.Store</code> object which will be used for storing the identifications of already processed messages.<br/> <b>This store is only used with the POP3 protocol and if unseen mails are processed only.</b></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
mail:sender
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connection | java.lang.String | <p>Specifies the connection URI used to connect to a mail server. <br /><br /> <b><u>Templates:</u></b> <br /> nbsp; i><rotocol>//<ser><ost>:<ort>/<older>?password=<assword>/i> <br /><b> nbsp; nbsp; nbsp;OR</b><br/> nbsp; i><rotocol>//<ost>:<ort>/<older>?user=<ser>password=<assword>/i> <br /><br /> <b><u>Details:</u></b><br /><br/> <table border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"> <tr> <td width="40%" align="left"><b><u>Name</u></b></td> <td width="60%" align="left"><b><u>Description</u></b></td> </tr> <tr> <td>protocol</td> <td>the protocol to use (example: pop3 or imap)</td> </tr> <tr> <td>user</td> <td>the user name used to log into an account</td> </tr> <tr> <td>host</td> <td>the name or ip address of the mail server</td> </tr> <tr> <td>port</td> <td>the port number to use (optional)</td> </tr> <tr> <td>folder</td> <td>the folder to poll from (optional)</td> </tr> <tr> <td>password</td> <td>the password for the login</td> </tr> </table> <br/> <b><u>Example:</u></b><br /> nbsp; i>smtp://lhein@myserver?password=myPass</i><br /></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| customProperties | java.util.Map | <p>Specifies a <code>java.util.Map</code> which may contain additional properties for the connection. <br/> <br/><b><u>Example for disabling TOP for POP3 headers:</u></b><br /> i><b>key</b>: "mail.pop3.disabletop"</i> <br /> i><b>value</b>: "true"</i></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| customTrustManagers | java.lang.String | <p>Specifies one or more trust manager classes separated by a semicolon (<b>;</b>).<br/> These classes have to implement the <code>Trustmanager</code> interface and need to provide an empty default constructor to be valid.<br/><br /> If you want to accept all security certificates without a check you may consider using the <code>DummyTrustManager</code> class. It is actually only an empty stub without any checking logic. <br/><b>But be aware that this will be a security risk in production environments. </b></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| debugMode | boolean | <p>Specifies if the JavaMail is run in <code>DEBUG</code> mode. This means that while connecting to server and processing mails a detailed log is written to debug output. <br /> This mode is very handy if you are experiencing problems with your mail server connection and you want to find out what is going wrong in communication with the server. <br /><br /> nbsp; b>true</b> - <i>the debug mode is <b>enabled</b></i> <br /> nbsp; b>false</b> - <i>the debug mode is <b>disabled</b></i></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>false</b></i><br/><br/> |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| ignoreMessageProperties | (java.lang.Object)\* | <p>Specifies a <code>java.util.List</code> which may contain message properties to skip. <br/> <br/><b><u>Example for skipping all kind of addresses from the normalized message:</u></b><br /> i><b>value</b>: "org.apache.servicemix.mail.to"</i> <br /> i><b>value</b>: "org.apache.servicemix.mail.cc"</i> <br /> i><b>value</b>: "org.apache.servicemix.mail.bcc"</i> <br /> i><b>value</b>: "org.apache.servicemix.mail.from"</i> <br /> i><b>value</b>: "org.apache.servicemix.mail.replyto"</i> <br /></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.mail.marshaler.AbstractMailMarshaler | <p>With this method you can specify a marshaler class which provides the logic for converting a normalized message into a mail. This class has to extend the abstract class <code>AbstractMailMarshaler</code> or an extending class. If you don't specify a marshaler, the <code>DefaultMailMarshaler</code> will be used.</p> |
| receiver | java.lang.String | <p>Specifies the receiver address(es) of the mail which is being sent.</p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| sender | java.lang.String | <p>Specifies the sender address of the mail which is being sent.</p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>no-reply@localhost</b></i><br/><br/> |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
servicemix-osworkflow
Overview
The ServiceMix OSWorkflow component provides workflow functionality to the ESB. You can specify one or more workflows and it's processing will start when a valid message is received.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/osworkflow/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:osworkflow="http://servicemix.apache.org/osworkflow/1.0">
<!-- add osworkflow:endpoint here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-osworkflow component defines a single endpoint type:
osworkflow:endpoint :: The endpoint will receive messages from the NMR and will then start the processing of the workflow.
osworkflow:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| action | int | The initial action to trigger in the workflow. |
| caller | java.lang.String | The caller user name to be used when executing the workflow. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| workflowName | java.lang.String | The name of the workflow to be used for handling the exchange. |
servicemix-quartz
Overview
The servicemix-quartz component is a standard JBI Service Engine able to schedule and trigger jobs using the great Quartz scheduler.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/quartz/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:osworkflow="http://servicemix.apache.org/quartz/1.0">
<!-- add quartz:endpoint here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-quartz component defines a single endpoint type:
quartz:endpoint :: The quartz endpoint can be used to fire message exchanges at a given (recurrent) time.
quartz:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| calendars | java.util.Map | A map with {@link org.quartz.Calendar} instances to define the trigger schedule. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| jobDetail | org.quartz.JobDetail | Set a custom JobDetail bean to be used in the triggered events. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.quartz.support.QuartzMarshaler | Set a custom marshaler class to translate the JobDetail information into a normalized message. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
| trigger | org.quartz.Trigger | A single {@link org.quartz.Trigger} instance to define the trigger schedule. |
| triggers | (java.lang.Object)\* | A list of of {@link org.quartz.Trigger} instances to allow configuring multiple schedules for the same endpoint. |
servicemix-saxon
Overview
The servicemix-saxon component is a standard JBI Service Engine for XSLT / XQuery. This component is based on Saxon and supports XSLT 2.0 and XPath 2.0, and XQuery 1.0.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/saxon/1.0. This is an example of xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix saxon.
<beans xmlns:saxon="http://servicemix.apache.org/saxon /1.0">
<!-- add saxon:xslt, saxon:xquery or saxon:proxy definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-saxon component defines these endpoints:
saxon:xslt: Translates the in message content using XSLT to send back the translated content in the out message
saxon:proxy: Acts as a proxy for an endpoint, translating the message passed to/from the endpoint using XSLT
saxon:xquery: Use xquery to extract parts of the XML
Endpoint saxon:xslt
The XSLT endpoint can be used to apply an XSLT stylesheet to the incoming exchange and will return the transformed result as the output message.
<saxon:xslt service="test:xslt" endpoint="endpoint"
resource="classpath:transform.xsl" />
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| configuration | net.sf.saxon.Configuration | Additional configuration for the Saxon XSL-T/XQuery processor. |
| copyAttachments | boolean | Copy attachments into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| copyProperties | boolean | Copy properties into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| copySubject | boolean | Copy the security subject into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| expression | org.apache.servicemix.expression.Expression | Expression to dynamically determine the stylesheet to use for processing the exchange. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| parameters | java.util.Map | Add parameter names and values that are available during XSL/XQuery processing. |
| reload | boolean | Sets whether the endpoint should reload the resource each time it is used. A value of <code>true</code> will ensure that the resource is not cached which can be useful if the resource is updated regularly and is stored outside of the service unit. |
| resource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Spring Resource for the XSL-T stylesheet or XQuery file to use. |
| result | java.lang.String | The output result type, possible values are dom, bytes, string. Defaults to dom. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| sourceTransformer | org.apache.servicemix.jbi.jaxp.SourceTransformer | Set a SourceTransformer instance to use for handling XML conversions. |
| transformerFactory | javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory | Set a transform factory, e.g. for injecting a custom transformer configuration or implementation. |
| useDomSourceForContent | java.lang.Boolean | Convert the message body Source into a DOMSource. Defaults to <code>false</true>. |
| useDomSourceForXslt | boolean | Convert the XSL-T stylesheet Source into a DOMSource. Defaults to <code>true</true>. |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Resource referring to the WSDL resource that defines this endpoint. |
Mandatory properties
The endpoint requires one of these two properties to be specified:
| Attribute | Type | description |
|---|---|---|
| resource | (Spring resource) | the spring resource pointing to the XSLT stylesheet |
| expression | (ServiceMix expression) | expression used to dynamically load the stylesheet |
Optional properties
| Attribute | Type | description |
|---|---|---|
| wsdlResource | (Spring resource) | if set, the wsdl will be retrieved from the given Spring resource |
| transformerFactory | (TransformerFactory, defaults to the Saxon implementation) | TraX factory to create transformers |
| configuration | (Saxon configuration) | Saxon configuration object |
| result | (String, defaults to dom) | Allows specifying the output result type, possible values are dom, bytes, string |
| copyAttachments, copyProperties and copySubject | (default to true | Configure to copy message attachments, properties and security subject over to the result message |
| useDomSourceForXslt | (defaults to true | when set to true, forces the transformation of the xslt stylesheet into a DOM document before giving it to the transformer |
| useDomSourceForContent | (defaults to false) | when set to true, forces the transformation of the incoming JBI message into a DOM document before giving it to the transformer |
| parameters | a Map | containing additional parameters to give to the transformation engine |
Using properties and parameters
All properties defined on the JBI exchange and input JBI message will be available for use inside the XSLT stylesheet as parameters.
In addition to those properties and the one specified in the parameters property on the endpoint, the following objects are also available:
exchange : the JBI exchange
in : the input JBI NormalizedMessage
component : the XsltEndpoint instance being called
Below is an example that demonstrates how the properties of the exchange and normalized message can be accessed from inside the xslt.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1253"?>
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform" version="2.0"
xmlns:class="http://saxon.sf.net/java-type"
xmlns:me="java:javax.jbi.messaging.MessageExchange"
xmlns:nm="java:javax.jbi.messaging.NormalizedMessage">
<xsl:output method="xml" indent="yes" encoding="ISO-8859-1"/>
<xsl:param name="exchange" as="class:javax.jbi.messaging.MessageExchange"/>
<xsl:param name="in" as="class:javax.jbi.messaging.NormalizedMessage"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
<message>
<!-- The value of messageId will be read from thr property MSG_ID of the "in" NormalizedMessage -->
<messageId>
<xsl:value-of select="nm:getProperty($in, 'MSG_ID')"/>
</messageId>
</message>
</xsl:stylesheet>
All those parameters can be accessed using XSLT standard ways using <xsl:param/>.
Endpoint saxon:proxy
One common use case is the need to transform a request coming from a service and send it to another service and do the same with the response. A simple example is the need to translate the request and responses between two SOAP endpoints. Such a use case could be implemented using two XSLT endpoints and an EIP StaticRoutingSlip. However, there are some drawbacks, as the operation is lost in the process, and a static routing slip can not be used to process InOnly exchanges.
<saxon:proxy service="test:proxy" endpoint="endpoint"
resource="classpath:transform-in.xsl"
outResource="classpath:transform-out.xsl"
faultResource="classpath:transform-fault.xsl">
<saxon:target>
<saxon:exchange-target service="test:echo" />
</saxon:target>
</saxon:proxy>
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| configuration | net.sf.saxon.Configuration | Additional configuration for the Saxon XSL-T/XQuery processor. |
| copyAttachments | boolean | Copy attachments into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| copyProperties | boolean | Copy properties into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| copySubject | boolean | Copy the security subject into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| expression | org.apache.servicemix.expression.Expression | Expression to dynamically determine the stylesheet to use for processing the exchange. |
| faultResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Spring Resource for the XSL-T stylesheet or XQuery file to use for transforming the 'fault' message. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| outResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Spring Resource for the XSL-T stylesheet or XQuery file to use for transforming the 'out' message. |
| parameters | java.util.Map | Add parameter names and values that are available during XSL/XQuery processing. |
| reload | boolean | Sets whether the endpoint should reload the resource each time it is used. A value of <code>true</code> will ensure that the resource is not cached which can be useful if the resource is updated regularly and is stored outside of the service unit. |
| resource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Spring Resource for the XSL-T stylesheet or XQuery file to use. |
| result | java.lang.String | The output result type, possible values are dom, bytes, string. Defaults to dom. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| sourceTransformer | org.apache.servicemix.jbi.jaxp.SourceTransformer | Set a SourceTransformer instance to use for handling XML conversions. |
| store | org.apache.servicemix.store.Store | Configure a custom Store implementation to store correlation information. Usually, a store factory is configured instead of a store. Defaults to {@link org.apache.servicemix.store.memory.MemoryStore}. |
| storeFactory | org.apache.servicemix.store.StoreFactory | Configure a custom StoreFactory implementation to store correlation information. Defaults to {@link org.apache.servicemix.store.memory.MemoryStoreFactory}. |
| target | org.apache.servicemix.saxon.support.ExchangeTarget | Set the target endpoint that is being proxied by the <code>xslt:proxy</code> endpoint. |
| transformerFactory | javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory | Set a transform factory, e.g. for injecting a custom transformer configuration or implementation. |
| useDomSourceForContent | java.lang.Boolean | Convert the message body Source into a DOMSource. Defaults to <code>false</true>. |
| useDomSourceForXslt | boolean | Convert the XSL-T stylesheet Sources into a DOMSource. Defaults to <code>true</true>. |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Resource referring to the WSDL resource that defines this endpoint. |
Mandatory properties
Depending on the MEP, you have to set one or more XSL stylesheets to be used for converting the message payloads:
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| resource | Spring resource | the XSLT stylesheet used to transform the input message |
| outResource | Spring resource | the XSLT stylesheet used to transform the output message |
| faultResource | Spring resource | the XSLT stylesheet used to transform the fault message |
| expression | ServiceMix expression | used to dynamically load the stylesheet. If set, it will prevail against all resource, outResource and faultResource attributes |
You also have to specify the target service that should be invoked from this endpoint:
target : ExchangeTarget that specifies the target service for the proxy endpoint
Optional properties
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| wsdlResource | Spring resource | if set, the wsdl will be retrieved from the given (Spring resource) |
transformerFactory (defaults to the Saxon implementation) :: TraX TransformerFactory to create transformers | configuration | (Saxon configuration) |
| result | (defaults to dom) :: Allows specifying the output result type, possible values are dom, bytes, string | copyAttachments, copyProperties and copySubject |
Endpoint saxon:xquery
The XQuery endpoint can be used to apply a selected XQuery to the input document.
<saxon:xquery service="test:xquery" endpoint="endpoint"
resource="classpath:query.xq" />
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| configuration | net.sf.saxon.Configuration | Additional configuration for the Saxon XSL-T/XQuery processor. |
| copyAttachments | boolean | Copy attachments into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| copyProperties | boolean | Copy properties into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| copySubject | boolean | Copy the security subject into the resulting normalized message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| expression | org.apache.servicemix.expression.Expression | Expression to dynamically determine the stylesheet to use for processing the exchange. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| outputProperties | java.util.Properties | Configure serialization properties, in JAXP format, if the result is to be serialized. This parameter can be defaulted to null. |
| parameters | java.util.Map | Add parameter names and values that are available during XSL/XQuery processing. |
| query | java.lang.String | Configure the XQuery expression to evaluate. |
| reload | boolean | Sets whether the endpoint should reload the resource each time it is used. A value of <code>true</code> will ensure that the resource is not cached which can be useful if the resource is updated regularly and is stored outside of the service unit. |
| resource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Spring Resource for the XSL-T stylesheet or XQuery file to use. |
| result | java.lang.String | The output result type, possible values are dom, bytes, string. Defaults to dom. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| sourceTransformer | org.apache.servicemix.jbi.jaxp.SourceTransformer | Set a SourceTransformer instance to use for handling XML conversions. |
| wsdlResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Resource referring to the WSDL resource that defines this endpoint. |
Mandatory properties
You need to specify one of query, resource or expression
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| query | String | containing the inlined XQuery expression |
| resource | Spring resource | resource pointing to the XQuery |
| expression | ServiceMix expression | expression to dynamically load the xquery |
Optional properties
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| wsdlResource | (Spring resource) | WSDL describing the endpoint |
| outputProperties | Map | Saxon specific output properties |
| configuration | (Saxon configuration) | Saxon configuration object |
| result | (defaults to dom) | Allows specifying the output result type, possible values are dom, bytes, string |
| copyAttachments, copyProperties and copySubject | (default to true) | Configure to copy message attachments, properties and security subject over to the result message |
Sample configurations
Dynamic stylesheet selection (saxon:xslt)
This endpoint configuration will dynamically load the XSL-T resource that is specified in the xslt.source property on the NormalizedMessage
<saxon:xslt service="test:xslt-dynamic" endpoint="endpoint">
<saxon:expression>
<bean class="org.apache.servicemix.expression.PropertyExpression">
<property name="property" value="xslt.source" />
</bean>
</saxon:expression>
</saxon:xslt>
Using parameters in the XSL-T stylesheet (saxon:xslt)
You can define a Map of parameters on the saxon:xslt endpoint.
<saxon:xslt service="test:xslt-params" endpoint="endpoint"
resource="classpath:parameter-test.xsl">
<property name="parameters">
<map>
<entry key="stringParam" value="cheeseyCheese"/>
<entry key="integerParam">
<bean class="java.lang.Integer">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="4002"/>
</bean>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</saxon:xslt>
In the XSL file, you can access the parameter values with <xsl:param/>. You can also access headers on the NormalizedMessage (like e.g. org.apache.servicemix.file) with the same syntax.
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl='http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform' version='1.0'>
<xsl:param name="stringParam"/>
<xsl:param name="integerParam"/>
<xsl:param name="org.apache.servicemix.file" />
...
</xsl:stylesheet>
Inlined XQuery and specific output configuration (saxon:xquery)
<saxon:xquery service="test:xquery-inline" endpoint="endpoint">
<saxon:query>
for $x in /bookstore/book
where $x/price > 30
return $x/title
</saxon:query>
<saxon:outputProperties>
<saxon:property key="{http://saxon.sf.net/}wrap-result-sequence">yes</saxon:property>
</saxon:outputProperties>
</saxon:xquery>
Dynamic XQuery selection (saxon:xquery)
This endpoint configuration will dynamically load the XQuery resource that is specified in the xquery.source property on the NormalizedMessage
<saxon:xquery service="test:xquery-dynamic" endpoint="endpoint">
<saxon:expression>
<bean class="org.apache.servicemix.expression.PropertyExpression">
<property name="property" value="xquery.source" />
</bean>
</saxon:expression>
</saxon:xquery>
servicemix-scripting
Overview
The ServiceMix Scripting component provides support for processing scripts using JSR-223 compliant scripting languages.
The component is currently shipping with:
Groovy (1.5.6)
JRuby (1.1.2)
Rhino JavaScript (1.7R1)
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/scripting/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:scripting="http://servicemix.apache.org/scripting/1.0">
<!-- add scripting:endpoint here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-scripting component defines a single endpoint type:
scripting:endpoint :: The scripting endpoint can be used to use scripts to handle exchanges or send new exchanges
scripting:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bindings | java.util.Map | A Map with additional variables that are made available during script execution. |
| copyAttachments | boolean | Copy the attachments into the 'out' message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| copyProperties | boolean | Copy the properties into the 'out' message. Defaults to <code>true</code>. |
| disableOutput | boolean | Set this flag to true to <code>true</code> to avoid sending back a response message. Defaults to <code>false</code> |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| language | java.lang.String | The scripting language to be used. Defaults to <code>autodetect</code> to determine the language by the script file extension. |
| logResourceBundle | java.lang.String | The resource bundle to use when logging internationalized messages. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.scripting.ScriptingMarshalerSupport | Custom marshaler implementation to handle startup/shutdown, loading the script code and registering additional user beans. |
| script | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Spring Resource referring to the script location. |
| scriptLogger | java.util.logging.Logger | returns the script logger |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | Target endpoint for the output exchange that is created by the script. |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Target interface for the output exchange that is created by the script. |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Target operation for the output exchange that is created by the script. |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | Target service for the output exchange that is created by the script. |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | URI for configuring target service/endpoint/interface for the exchange that is created by the script. |
servicemix-snmp
Overview
The ServiceMix SNMP component provides support for receiving SNMP events via the enterprise service bus by using the SNMP4J library.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/snmp/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:snmp="http://servicemix.apache.org/snmp/1.0">
<!-- add snmp:poller or snmp:sender definitions here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-snmp component defines two endpoint types:
snmp:poller :: Periodically polls a device status using SNMP and sends the OIDs as a JBI MessageExchange
snmp:trap-consumer :: Consumes an SNMP trap message and sends the OIDs as a JBI MessageExchange
snmp:poller
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| address | java.lang.String | <p>Specifies the connection URI used to connect to a snmp capable device. <br /><br /> <b><u>Template:</u></b> <br /> nbsp; i><rotocol><ost><ort>/i> <br /><br /> <b><u>Details:</u></b><br /><br/> <table border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"> <tr> <td width="40%" align="left"><b><u>Name</u></b></td> <td width="60%" align="left"><b><u>Description</u></b></td> </tr> <tr> <td>protocol</td> <td>the protocol to use (udp or tcp)</td> </tr> <tr> <td>host</td> <td>the name or ip address of the snmp capable device</td> </tr> <tr> <td>port</td> <td>the port number to use</td> </tr> </table> <br/> <b><u>Example:</u></b><br /> nbsp; i>udp:192.168.2.122/161</i></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| concurrentPolling | boolean | Sets whether more than one poll can be active at a time (true means yes). Default value is <code>false</code>. |
| delay | long | Sets the amount of time in milliseconds that the endpoint should wait before making the first poll. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| firstTime | java.util.Date | Sets the date on which the first poll will be executed. If a delay is also set using <code>setDelay</code>, the delay interval will be added after the date specified. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.snmp.marshaler.SnmpMarshalerSupport | <p>Specifies a marshaler class which provides the logic for converting a snmp response into a normalized message. This class has to implement the <code>SnmpMarshalerSupport</code> interface. If you don't specify a marshaler, the <code>DefaultSnmpMarshaler</code> will be used.</p> |
| oids | (java.lang.Object)\* | <p>Specifies a reference to a list of OID values which will be used for the snmp request. You have two possibilities how to specify the value: <br /><br /> i>a) referencing to a file containing a list of OID values separated by a line feed <br/> nbsp; nbsp;or<br/> i>b) defining a coma (<b>,</b>) separated list of OID values <br /><br /> <b><u>Examples:</u></b><br /> nbsp; i>a) oids="classpath:myOids.txt"<br /> nbsp; nbsp; nbsp; ids="file:/home/lhein/snmp/device_a/oids.txt"<br/> <br /> nbsp; i>b) oids="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 , 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.5.1 , 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.5.1.1.1 , 1.3.6.1.2.1.43.5.1.1.11.1"</i></p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>null</b></i><br/><br/> |
| period | long | Sets the number of milliseconds between polling attempts. |
| retries | int | <p>Specifies the connection retries.</p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>2</b></i><br/><br/> |
| scheduler | org.apache.servicemix.common.scheduler.Scheduler | Set a custom Scheduler implementation if you need more fine-grained control over the polling schedule. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| snmpCommunity | java.lang.String | <p>Specifies the snmp community to use.</p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>"public"</b></i><br/><br/> |
| snmpVersion | int | <p>Specifies the snmp protocol version to use.</p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>0 (version 1)</b></i><br/><br/> |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
| timeout | int | <p>Specifies the connection time out in milliseconds.</p> <i> nbsp; he default value is <b>1500</b></i><br/><br/> |
vfs:trap-consumer
Endpoint properties
servicemix-validation
Overview
The ServiceMix Validation component provides schema validation of documents using JAXP 1.3 and XMLSchema or RelaxNG.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/validation/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:scripting="http://servicemix.apache.org/validation/1.0">
<!-- add validation:endpoint here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-validation component defines a single endpoint type:
validation:endpoint :: Validates the incoming XML message - can be configured to fail the exchange or to send validation errors back to the sender in the message body.
validation:endpoint
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| errorHandlerFactory | org.apache.servicemix.validation.handler.MessageAwareErrorHandlerFactory | Set a custom error handler to deal with validation errors. Defaults to a <code>CountingErrorHandlerFactory</code>. |
| handlingErrorMethod | java.lang.String | Configure how validation errors should be handled. Default value is <code>FAULT_JBI</code>. <dl> <dt><code>FAULT_JBI</code></dt> <dd>A jbi exception is thrown on validation errors (depending on used MEP)</dd> <dt><code>FAULT_FLOW</code></dt> <dd>The validation result will be sent in out / fault message (depending on used MEP)</dd> </dl> |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| noNamespaceSchemaResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Set the validation schema to be used when no namespace is specified. |
| schema | javax.xml.validation.Schema | Set the validation schema instance. |
| schemaLanguage | java.lang.String | Set the validation schema language. Defaults to <code>http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema</code> |
| schemaResource | org.springframework.core.io.Resource | Set the validation schema as a Spring Resource. |
| schemaSource | javax.xml.transform.Source | Set the validation schema as an XML Source. |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
servicemix-vfs
Overview
The ServiceMix VFS component provides support for reading from and writing to virtual file systems via the enterprise service bus by using the Apache commons-vfs library.
Namespace and xbean.xml
The namespace URI for the servicemix-bean JBI component is http://servicemix.apache.org/vfs/1.0. This is an example of an xbean.xml file with a namespace definition with prefix bean.
<beans xmlns:vfs="http://servicemix.apache.org/vfs/1.0">
<!-- add vfs:poller or vfs:sender here -->
</beans>
Endpoint types
The servicemix-vfs component defines two endpoint types:
vfs:poller :: Periodically polls a directory on one of the VFS-supported file systems for files and sends an exchange for every file
vfs:sender :: Writes the contents of an exchange to a file on one of the VFS-supported file systems
vfs:poller
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| comparator | java.util.Comparator | Specifies a <code>Comparator</code> object. |
| component | org.apache.servicemix.common.DefaultComponent | the default component |
| concurrentExchange | boolean | |
| concurrentPolling | boolean | Sets whether more than one poll can be active at a time (true means yes). Default value is <code>false</code>. |
| delay | long | Sets the amount of time in milliseconds that the endpoint should wait before making the first poll. |
| deleteFile | boolean | Specifies if files should be deleted after they are processed. Default value is <code>true</code>. |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| fileSystemManager | org.apache.commons.vfs.FileSystemManager | sets the file system manager |
| firstTime | java.util.Date | Sets the date on which the first poll will be executed. If a delay is also set using <code>setDelay</code>, the delay interval will be added after the date specified. |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| lockManager | org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.LockManager | Bean defining the class implementing the file locking strategy. This bean must be an implementation of the <code>org.apache.servicemix.locks.LockManager</code> interface. By default, this will be set to an instances of <code>org.apache.servicemix.common.locks.impl.SimpleLockManager</code>. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler | Specifies a <code>FileMarshaler</code> object that will marshal file data into the NMR. The default file marshaller can read valid XML data. <code>FileMarshaler</code> objects are implementations of <code>org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler</code>. |
| path | java.lang.String | Specifies a String object representing the path of the file/folder to be polled.Examples:
|
vfs:sender
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| fileSystemManager | org.apache.commons.vfs.FileSystemManager | sets the file system manager |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler | Specifies a <code>FileMarshaler</code> object that will marshal file data into the NMR. The default file marshaller can read valid XML data. <code>FileMarshaler</code> objects are implementations of <code>org.apache.servicemix.components.util.FileMarshaler</code>. |
| path | java.lang.String | Specifies a String object representing the path of the file/folder to be polled.Examples:
|
servicemix-wsn2005
Overview
The servicemix-wsn2005 is a standard JBI Service Engine which implements the WS-Notification specification from Oasis.
servicemix-xmpp
Overview
The ServiceMix XMPP component is used to communicate with XMPP (Jabber) servers through the JBI bus.
xmpp:receiver
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| createAccount | boolean | <p>Specify here if you want to create an account for the user if the user is currently not existing on the XMPP server.</p> |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| filter | org.jivesoftware.smack.filter.PacketFilter | <p>Here you can define a <code>PacketFilter</code> to use for filtering XMPP packets. |
| host | java.lang.String | <p>With that method you can specify the host name of the XMPP server as hostname or ip address.</p> |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| login | boolean | <p>Here you can specify if the user should login to the server or not. Not logging in means that endpoint itself will be created but it will be inactive.</p> |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.xmpp.marshaler.XMPPMarshalerSupport | <p>With this method you can specify a marshaler class which provides the logic for converting an xmpp message into a normalized message. This class has to implement the interface <code>XMPPMarshalerSupport</code> or another class which implements it. If you don't specify a marshaler, the <code>DefaultXMPPMarshaler</code> will be used.</p> |
| password | java.lang.String | <p>This method sets the password for connecting to the XMPP server.</p> |
| port | int | <p>This method will set the port number for the XMPP connection. If nothing is defined the default XMPP port number 5222 will be used.</p> |
| proxyHost | java.lang.String | <p>Here you can specify the hostname or ip address of a proxy to be used to connect to the XMPP server. If you don't define this no proxy is used.</p> |
| proxyPass | java.lang.String | <p>If your proxy needs authentication you can specify here the user password. Leave this undefined if your proxy does not need authentication.</p> |
| proxyPort | java.lang.String | <p>Here you can specify the port of the proxy server. If you do not define this the default port (3128) will be used. |
| proxyType | java.lang.String | <p>Here you can specify the type of proxy you have. Possible values are: <code>NONE</code>, <code>HTTP</code>, <code>SOCKS4</code>, <code>SOCKS5</code> |
| proxyUser | java.lang.String | <p>If your proxy needs authentication you can specify here the user name. Leave this undefined if your proxy does not need authentication.</p> |
| resource | java.lang.String | <p>Specify here the resource string to submit to the XMPP server. Usually you define the identifier of the XMPP client here.</p> |
| room | java.lang.String | <p>Specify here an optional room to join. If set, the user will join that room and listens to messages there.</p> |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| targetEndpoint | java.lang.String | the name of the endpoint to which requests are sent |
| targetInterface | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the interface to which requests are sent |
| targetOperation | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the operation to which requests are sent |
| targetService | javax.xml.namespace.QName | the QName of the service to which requests are sent |
| targetUri | java.lang.String | Set the target service/endpoint/interface using a URI. |
| user | java.lang.String | <p>This method if used to specify the user name to use for connecting to the XMPP server. It is not required that this user already exists but if not then the server should allow registration of new users and this user should not already exist with another password.</p> |
xmpp:sender
Endpoint properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| createAccount | boolean | <p>Specify here if you want to create an account for the user if the user is currently not existing on the XMPP server.</p> |
| endpoint | java.lang.String | The name of the endpoint. |
| host | java.lang.String | <p>With that method you can specify the host name of the XMPP server as hostname or ip address.</p> |
| interfaceName | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the interface exposed by the endpoint. |
| login | boolean | <p>Here you can specify if the user should login to the server or not. Not logging in means that endpoint itself will be created but it will be inactive.</p> |
| marshaler | org.apache.servicemix.xmpp.marshaler.XMPPMarshalerSupport | <p>With this method you can specify a marshaler class which provides the logic for converting an xmpp message into a normalized message. This class has to implement the interface <code>XMPPMarshalerSupport</code> or another class which implements it. If you don't specify a marshaler, the <code>DefaultXMPPMarshaler</code> will be used.</p> |
| participant | java.lang.String | <p>Specify here an optional participant to send messages to. You have to define a room or participant in order to have send function working.</p> |
| password | java.lang.String | <p>This method sets the password for connecting to the XMPP server.</p> |
| port | int | <p>This method will set the port number for the XMPP connection. If nothing is defined the default XMPP port number 5222 will be used.</p> |
| proxyHost | java.lang.String | <p>Here you can specify the hostname or ip address of a proxy to be used to connect to the XMPP server. If you don't define this no proxy is used.</p> |
| proxyPass | java.lang.String | <p>If your proxy needs authentication you can specify here the user password. Leave this undefined if your proxy does not need authentication.</p> |
| proxyPort | java.lang.String | <p>Here you can specify the port of the proxy server. If you do not define this the default port (3128) will be used. |
| proxyType | java.lang.String | <p>Here you can specify the type of proxy you have. Possible values are: <code>NONE</code>, <code>HTTP</code>, <code>SOCKS4</code>, <code>SOCKS5</code> |
| proxyUser | java.lang.String | <p>If your proxy needs authentication you can specify here the user name. Leave this undefined if your proxy does not need authentication.</p> |
| resource | java.lang.String | <p>Specify here the resource string to submit to the XMPP server. Usually you define the identifier of the XMPP client here.</p> |
| room | java.lang.String | <p>Specify here an optional room to join. If set, the user will join that room and listens to messages there.</p> |
| service | javax.xml.namespace.QName | The qualified name of the service the endpoint exposes. |
| user | java.lang.String | <p>This method if used to specify the user name to use for connecting to the XMPP server. It is not required that this user already exists but if not then the server should allow registration of new users and this user should not already exist with another password.</p> |